Others like the crippled lamb Features >>
About the Book
"The Crippled Lamb" is a heartwarming children's book written by Max Lucado. It tells the story of a lamb named Joshua who feels different from the others because he is born with a crippled leg. Despite feeling left out, he eventually discovers that his uniqueness is a gift from God, and he plays a special role in the birth of Baby Jesus. The book teaches valuable lessons about acceptance, friendship, and the true meaning of Christmas.
John Alexander Dowie
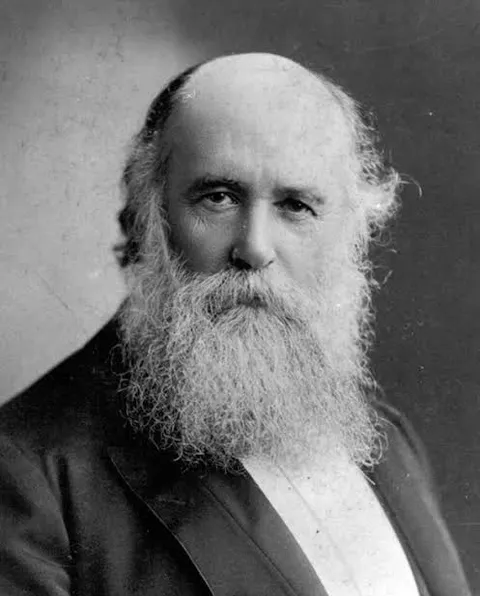 By John Alexander Dowie (1847 – 1907)
I sat in my study in the parsonage of the Congregational Church at Newtown, a suburb of the beautiful city of Sydney, Australia. My heart was very heavy, for I had visited the sick and dying beds of more than thirty of my flock, and I had cast the dust to its kindred dust into more than forty graves within a few weeks. Where, oh where, was He Who used to heal His suffering children? No prayer for healing seemed to reach His ear, and yet I knew His hand had not been shortened. Still it did not save from death even those for whom there was so much in life to live for God and others. Strong men, fathers, good citizens, and more than all, true Christians sickened with a putrid fever, suffered nameless agonies, passed into delirium, sometimes with convulsions, and then died.
Oh, what aching voids were left in many a widowed or orphaned heart. There were many homes where, one by one, the little children, the youths and the maidens lay stricken, and after a hard struggle with the foul disease, they too, lay cold and dead. It seemed sometimes as if I could almost hear the triumphant mockery of evil ringing in my ear whilst I spoke to the bereaved ones the words of Christian hope and consolation. Disease, the foul offspring of its father, Satan, and its mother Sin, was defiling and destroying the earthly temples of God’s children and there was no deliverance.
There I sat with sorrow-bowed head for my afflicted people, until the bitter tears came to relieve my burning heart. Then I prayed for some message, and oh, how I longed to hear some words from Him Who wept and sorrowed for the suffering long ago, a Man of Sorrows and Sympathies. The words of the Holy Ghost inspired In Acts 10:38, stood before me all radiant with light, revealing Satan as the Defiler, and Christ as the Healer. My tears were wiped away, my heart strong, I saw the way of healing, and the door thereto was opened wide, so I said, “God help me now to preach the Word to all the dying around, and tell them how Satan still defiles, and Jesus still delivers, for He is just the same today.”
A loud ring and several raps at the outer door, a rush of feet, and there at my door stood two panting messengers who said, “Oh, come at once, Mary is dying; come and pray. “With just a feeling as a shepherd has who hears that his sheep are being torn from the fold by a cruel wolf, I rushed from my house, ran without my hat down the street, and entered the room of the dying maiden. There she lay groaning and grinding her clenched teeth in the agony of the conflict with the destroyer. The white froth, mingled with her blood, oozing from her pale and distorted mouth. I looked at her and then my anger burned. “Oh,” I thought, “for some sharp sword of heavenly temper keen to slay this cruel foe who is strangling that lovely maiden like an invisible serpent, tightening his deadly coils for a final victory.”
In a strange way, It came to pass; I found the sword I needed was in my hands, and in my hand I hold it still and never will I lay It down. The doctor, a good Christian man, was quietly walking up and down the room, sharing the mother’s pain and grief. Presently he stood at my side and said, “Sir, are not God’s ways mysterious?” Instantly the sword was flashed in my hand, the Spirit’s sword, the Word of God. “God’s way?!” I said, pointing to the scene of conflict, “How dare you call that God’s way of bringing His children home from earth to Heaven? No sir, that is the devil’s work and it is time we called on Him Who came to destroy the work of the devil, to slay that deadly foul destroyer, and to save this child. Can you pray, Doctor, can you pray the prayer of faith that saves the sick?” At once, offended at my words, my friend was changed, and saying,” You are too much excited, sir, it is best to say ‘God’s will be done,’” and he left the room.
Excited?! The word was quite inadequate for I was almost frenzied with divinely imparted anger and hatred of that foul destroyer, disease, which was doing Satan’s will. “It is not so,” I exclaimed, “no will of God sends such cruelty, and I shall never say ‘God’s will be done’ to Satan’s works, which God’s own Son came to destroy, and this is one of them.” Oh, how the Word of God was burning in my heart: “Jesus of Nazareth went about doing good, and healing all that were oppressed of the devil; for God was with Him.” And was not God with me? And was not Jesus there and all His promises true? I felt that it was even so, and turning to the mother I inquired,” Why did you send for me?” To which she answered, “Do pray, oh pray for her that God may raise her up.” So we prayed.
What did I say? It may be that I cannot recall the words without mistake, but words are in themselves of small importance. The prayer of faith may be a voiceless prayer, a simple heartfelt look of confidence into the face of Christ. At such moment, words are few, but they mean much, for God is looking at the heart. Still, I can remember much of that prayer unto this day, and asking God to aid, I will attempt to recall it. I cried, “Our Father, help! and Holy Spirit, teach me how to pray. Plead Thou for us, oh, Jesus, Savior, Healer, Friend, our Advocate with God the Father. Hear and heal, Eternal One! From all disease and death, deliver this sweet child of yours. I rest upon the Word. We claim the promise now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord that heals thee.’ Then heal her now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord, I change not.’ Unchanging God, then prove Yourself the healer now. The Word is true. ‘These signs shall follow them that believe in My Name, they shall lay hands on the sick, and they shall recover.’ And I believe and I lay hands in Jesus’ Name on her and claim this promise now. Your Word is true. ‘The prayer of faith shall save the sick. Trusting in You alone. I cry. Oh, save her now, for Jesus’ sake. Amen!”
Then, the maid lay in sleep so deep and sweet that the mother asked in a low whisper, “Is she dead?” “No,” I answered, in a whisper lower still. “Mary will live; the fever is gone. She is perfectly well and sleeping as an infant sleeps.” I was smoothing the long dark hair from her now peaceful brow, and feeling the steady pulsation of her heart and cool moist hands. I saw that Christ had heard, and that once more, as long ago in Peter’s house, “He touched her and the fever left her.” Turning to the nurse, I said, “Get me at once, please, a cup of cocoa and several slices of bread and butter.” Beside the sleeping maid we sat quietly and almost silently until the nurse returned, and then I bent over her and snapping my fingers called, “Mary!”
Instantly she woke, smiled and said, “Oh, sir, when did you come? I have slept so long;” then stretching her arms out to meet her mother’s embrace, she said, “Mother, I feel so well.” “And hungry, too?” I asked, pouring some of the cocoa in a saucer and offering it to her when cooled by my breath. “Yes, hungry too,” she answered with a little laugh, and drank and ate again, and yet again until all was gone. In a few minutes, she fell asleep, breathing easily and softly. Quietly thanking God. We left her bed and went to the next room where her brother and sister also lay sick of the same fever. With these two, we prayed and they were healed too. The following day all three were well and in a week or so they brought me a little letter and a gift of gold, two sleeve links with my monogram, which I wore for many years. As I went away from the home where Christ as the Healer had been victorious, I could not but have somewhat in my heart of the triumphant song that rang through Heaven, and yet I was not a little amazed at my own strange doings, and still more at my discovery that He is just the same today.
Excerpt from the Sermons of John Alexander Dowie Champions of Faith by Gordon Lindsay
By John Alexander Dowie (1847 – 1907)
I sat in my study in the parsonage of the Congregational Church at Newtown, a suburb of the beautiful city of Sydney, Australia. My heart was very heavy, for I had visited the sick and dying beds of more than thirty of my flock, and I had cast the dust to its kindred dust into more than forty graves within a few weeks. Where, oh where, was He Who used to heal His suffering children? No prayer for healing seemed to reach His ear, and yet I knew His hand had not been shortened. Still it did not save from death even those for whom there was so much in life to live for God and others. Strong men, fathers, good citizens, and more than all, true Christians sickened with a putrid fever, suffered nameless agonies, passed into delirium, sometimes with convulsions, and then died.
Oh, what aching voids were left in many a widowed or orphaned heart. There were many homes where, one by one, the little children, the youths and the maidens lay stricken, and after a hard struggle with the foul disease, they too, lay cold and dead. It seemed sometimes as if I could almost hear the triumphant mockery of evil ringing in my ear whilst I spoke to the bereaved ones the words of Christian hope and consolation. Disease, the foul offspring of its father, Satan, and its mother Sin, was defiling and destroying the earthly temples of God’s children and there was no deliverance.
There I sat with sorrow-bowed head for my afflicted people, until the bitter tears came to relieve my burning heart. Then I prayed for some message, and oh, how I longed to hear some words from Him Who wept and sorrowed for the suffering long ago, a Man of Sorrows and Sympathies. The words of the Holy Ghost inspired In Acts 10:38, stood before me all radiant with light, revealing Satan as the Defiler, and Christ as the Healer. My tears were wiped away, my heart strong, I saw the way of healing, and the door thereto was opened wide, so I said, “God help me now to preach the Word to all the dying around, and tell them how Satan still defiles, and Jesus still delivers, for He is just the same today.”
A loud ring and several raps at the outer door, a rush of feet, and there at my door stood two panting messengers who said, “Oh, come at once, Mary is dying; come and pray. “With just a feeling as a shepherd has who hears that his sheep are being torn from the fold by a cruel wolf, I rushed from my house, ran without my hat down the street, and entered the room of the dying maiden. There she lay groaning and grinding her clenched teeth in the agony of the conflict with the destroyer. The white froth, mingled with her blood, oozing from her pale and distorted mouth. I looked at her and then my anger burned. “Oh,” I thought, “for some sharp sword of heavenly temper keen to slay this cruel foe who is strangling that lovely maiden like an invisible serpent, tightening his deadly coils for a final victory.”
In a strange way, It came to pass; I found the sword I needed was in my hands, and in my hand I hold it still and never will I lay It down. The doctor, a good Christian man, was quietly walking up and down the room, sharing the mother’s pain and grief. Presently he stood at my side and said, “Sir, are not God’s ways mysterious?” Instantly the sword was flashed in my hand, the Spirit’s sword, the Word of God. “God’s way?!” I said, pointing to the scene of conflict, “How dare you call that God’s way of bringing His children home from earth to Heaven? No sir, that is the devil’s work and it is time we called on Him Who came to destroy the work of the devil, to slay that deadly foul destroyer, and to save this child. Can you pray, Doctor, can you pray the prayer of faith that saves the sick?” At once, offended at my words, my friend was changed, and saying,” You are too much excited, sir, it is best to say ‘God’s will be done,’” and he left the room.
Excited?! The word was quite inadequate for I was almost frenzied with divinely imparted anger and hatred of that foul destroyer, disease, which was doing Satan’s will. “It is not so,” I exclaimed, “no will of God sends such cruelty, and I shall never say ‘God’s will be done’ to Satan’s works, which God’s own Son came to destroy, and this is one of them.” Oh, how the Word of God was burning in my heart: “Jesus of Nazareth went about doing good, and healing all that were oppressed of the devil; for God was with Him.” And was not God with me? And was not Jesus there and all His promises true? I felt that it was even so, and turning to the mother I inquired,” Why did you send for me?” To which she answered, “Do pray, oh pray for her that God may raise her up.” So we prayed.
What did I say? It may be that I cannot recall the words without mistake, but words are in themselves of small importance. The prayer of faith may be a voiceless prayer, a simple heartfelt look of confidence into the face of Christ. At such moment, words are few, but they mean much, for God is looking at the heart. Still, I can remember much of that prayer unto this day, and asking God to aid, I will attempt to recall it. I cried, “Our Father, help! and Holy Spirit, teach me how to pray. Plead Thou for us, oh, Jesus, Savior, Healer, Friend, our Advocate with God the Father. Hear and heal, Eternal One! From all disease and death, deliver this sweet child of yours. I rest upon the Word. We claim the promise now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord that heals thee.’ Then heal her now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord, I change not.’ Unchanging God, then prove Yourself the healer now. The Word is true. ‘These signs shall follow them that believe in My Name, they shall lay hands on the sick, and they shall recover.’ And I believe and I lay hands in Jesus’ Name on her and claim this promise now. Your Word is true. ‘The prayer of faith shall save the sick. Trusting in You alone. I cry. Oh, save her now, for Jesus’ sake. Amen!”
Then, the maid lay in sleep so deep and sweet that the mother asked in a low whisper, “Is she dead?” “No,” I answered, in a whisper lower still. “Mary will live; the fever is gone. She is perfectly well and sleeping as an infant sleeps.” I was smoothing the long dark hair from her now peaceful brow, and feeling the steady pulsation of her heart and cool moist hands. I saw that Christ had heard, and that once more, as long ago in Peter’s house, “He touched her and the fever left her.” Turning to the nurse, I said, “Get me at once, please, a cup of cocoa and several slices of bread and butter.” Beside the sleeping maid we sat quietly and almost silently until the nurse returned, and then I bent over her and snapping my fingers called, “Mary!”
Instantly she woke, smiled and said, “Oh, sir, when did you come? I have slept so long;” then stretching her arms out to meet her mother’s embrace, she said, “Mother, I feel so well.” “And hungry, too?” I asked, pouring some of the cocoa in a saucer and offering it to her when cooled by my breath. “Yes, hungry too,” she answered with a little laugh, and drank and ate again, and yet again until all was gone. In a few minutes, she fell asleep, breathing easily and softly. Quietly thanking God. We left her bed and went to the next room where her brother and sister also lay sick of the same fever. With these two, we prayed and they were healed too. The following day all three were well and in a week or so they brought me a little letter and a gift of gold, two sleeve links with my monogram, which I wore for many years. As I went away from the home where Christ as the Healer had been victorious, I could not but have somewhat in my heart of the triumphant song that rang through Heaven, and yet I was not a little amazed at my own strange doings, and still more at my discovery that He is just the same today.
Excerpt from the Sermons of John Alexander Dowie Champions of Faith by Gordon Lindsay
Your First Years of Marriage
In many ways, we were a natural fit. My would-be husband and I both loved Jesus, studied his word, cherished worship through song, desired many children, longed to be hospitable, and valued the home and the wife’s joyful place in it. We both had Scandinavian heritage and understood the barbs that flew between Swedes and Norwegians. We both prized hard work — with an openness to risk-taking endeavors. As an engaged couple, with all we had going for us, it was hard for me to imagine what bumps we might face as we started down the road together. But that’s only because I underestimated how real and stubborn indwelling sin is. I thought external bumps in the road would be the obstacles — circumstances like finances or health issues or job difficulties — when really it was our own flesh that presented the biggest problems. Reflecting back on the first years of marriage and family, I commend three principles to ease the bumps and grease the wheels of joy in Christ in your marriage and family. 1. Let God Define ‘Normal’ We all come from unique backgrounds. Even two people who share a similar heritage, like my husband and I, have had vastly different childhoods. I grew up with 27 first cousins. I became an aunt at 14 and can’t really remember a time we didn’t have young children around our home (even though I was the youngest child in my family). My husband had four cousins and had rarely encountered an infant or toddler at close range prior to marrying into my family. This made for very different ideas of what “normal” felt and sounded like. I grew up on an acreage in a blue-collar town that bordered several rural communities. My mom grew up on a farm. My husband grew up in a first-ring suburb of a major metropolis. His dad grew up in the big city. We had very different conceptions of what the “outdoors” was for. For him, it was mainly for recreation and enjoyment — for hiking or biking or kayaking. For me, it was mainly for work — for mowing or burning the burn pile or doing animal chores. Our former “norms” can enrich our marriage, adding interest and laughter and providing opportunities to take something that’s been passed down and make it new. Or they can threaten the allegiance of our hearts. If what was normal to us in our childhood becomes the ultimate standard for our marriage, we have misplaced our loyalties. We need to be led by the only authoritative and inerrant guide to life and marriage that we have: All Scripture is breathed out by God and profitable for teaching, for reproof, for correction, and for training in righteousness, that the man of God may be complete, equipped for every good work. (2 Timothy 3:16–17) Including every good work in the sometimes thorny first years of marriage. In marriage, God is making something new: a new one-flesh union, that is, a new family. And when a husband and wife let God’s word define normal, the wife willingly comes under the leadership of her husband in submission, as Scripture directs her to reflect Christ’s church (Ephesians 5:22–25). Her family of origin may aid that process or hinder it, but in either case, a reprioritizing happens. For the husband, it means looking to Christ as the standard by which he loves and leads his wife, and adopting his previous family’s practices only inasmuch as they accord with Christ. “If God’s word is the norm, the authority, you will have solid common ground on which to stand, come what may.” When I was young, my mom gave me one primary piece of advice when it came to choosing a husband: “God’s word must be his authority.” It’s key advice for men and women, and I gladly pass it along to you. If God’s word is the norm, the authority — not the culture, not your friends’ opinions or your family’s traditions, not Netflix or social media — you will have solid common ground on which to stand, come what may. 2. Stay in Step with the Spirit Paul tells the Galatians, “If we live by the Spirit, let us also keep in step with the Spirit. Let us not become conceited, provoking one another, envying one another” (Galatians 5:25–26). It may seem unlikely for two people who love each other and have committed their lives to one another “for better or worse” to fall into conceit, envy, and provocation of one another — and yet it’s common enough in marriage. The lies of the world have primed us to believe that men and women are on two separate teams in life. Team Women must advocate for women, and Team Men (in a bit of irony) must also advocate for women (although many rebel against this). This means that, at least for those of us raised in the United States or the West, women are expected to compete with men. From a young age, girls are taught that how they rank is a function of whether or not they are beating the boys. This way of thinking infects both boys and girls. And while that attitude may lie dormant during dating or courtship, it will rear its head if not dealt with. In a husband, this can look like unrealistic expectations for his wife — treating her like another man who shouldn’t have any significant differences from him. For example, he may expect her to earn what he earns, or overlook the inherent vulnerability of pregnancy and caring for small children. In a wife, this can look like pulling out the measuring stick to keep track of all the ways she’s getting a raw deal compared to him. For example, she may envy the occasional out-to-eat work lunches while she eats with the kids at home, or she may resent that the care of small children falls mainly to her. These are deadly attitudes to maintain in a marriage. When we marry, the Spirit of God does something amazing: he makes us part of a new team. I was blessed to join Team Dodds — not Team Women, or Team Men, or Team Me. When something wonderful happens to the husband, the wife rejoices as though it has happened to her, because it has. When something difficult happens to the wife, the husband nurtures and defends her as though it has happened to him, because it has. How do we keep in step with the Spirit in marriage? By prayerfully and regularly confessing our sins, and by setting our minds on the things of the Spirit, with a special focus on Christ — his life, his words, and his ways (1 John 1:9; Romans 8:5). We walk in the Spirit of Christ when we conform to the way he’s designed the marriage: “‘a man shall leave his father and his mother and hold fast to his wife, and the two shall become one flesh.’ So they are no longer two but one flesh. What therefore God has joined together, let not man separate” (Matthew 19:5–6). 3. Share Your New Life with Others My husband and I were married in June 2002. By October, we were taking a class to join our local church. At the same time, we opened our home (the upstairs of a duplex) to host a small group of singles and couples. I was 21 and still finishing college. It may have seemed a bit premature for us to join a church we were so new to, or to host a small group made up of mostly strangers, but the church had a need and we were eager to help. We didn’t join the church or host a small group primarily as ways to establish a stronger marriage, but looking back, they were important in shaping the patterns and priorities of our life. “The hospitable people I know are hospitable with little and with much, in small spaces and in big.” Many young families think that hospitality will sprout when the timing is right — when they get a bigger place, or when the kids aren’t so little, or when the finances aren’t so tight, or when they get that one room cleaned out. I’ve never seen it happen that way. The hospitable people I know are hospitable with little and with much, in small spaces and in big, among babies and boomers, in a dirty kitchen and a clean one. Sharing your home with others — making food for them, stretching your grocery budget on their behalf, letting them into your bathroom, cleaning up after their messes, inviting them into your thoughts through conversation and listening to theirs — is shockingly intimate in a world where embodied presence is becoming rare. Paul tells the Thessalonian church that “being affectionately desirous of you, we were ready to share with you not only the gospel of God but also our own selves, because you had become very dear to us” (1 Thessalonians 2:8). When we invite others into our home, we give them a bit of “our own selves.” When a husband, wife, and their children offer their home and their “own selves” to others through hospitality, they are not robbing time or resources from each other; they are gaining by giving. Hospitality forms a family identity that is not navel-gazing, but focused on sharing the love of God in practical ways with others. I can think of little else that will form and establish a Christian family to be joyful and robust in the Lord for decades to come than to practice sharing your life with others. Don’t let your home or marriage or family be only private. “Welcome one another as Christ has welcomed you, for the glory of God” (Romans 15:7). A husband and wife who have made God’s word their norm and who are keeping in step with the Spirit will have much to share with others. Open your doors and welcome many to come taste of Christ’s goodness at your table. Article by Abigail Dodds







-160.webp)





