
Testimonies To The Church, Vol 1 Order Printed Copy
- Author: Ellen G White
- Size: 1.51MB | 544 pages
- |
Others like testimonies to the church, vol 1 Features >>

Crimes Of The Cross

The Great Visions Of Ellen G White
.epub-160.webp)
Daughter Of Destiny: Kathryn Kuhlman
-160.webp)
Foxes Book Of Martyrs (History Of The Lives, Sufferings, And Triumphant Deaths Of The Primitive Protestant Martyrs)
-160.webp)
Abraham: One Nomad's Amazing Journey Of Faith
-160.webp)
God's Generals (William J. Seymour)

The Spirit Of Prophecy Volume 3

Here I Stand

God's Generals - The Martyrs

Smith Wigglesworth: A Man Who Walked With God
About the Book
"Testimonies to the Church, Vol 1" by Ellen G. White is a compilation of guidance and advice from the author, a prominent figure in the Seventh-day Adventist church. The book contains messages addressing various issues within the church and provides spiritual encouragement and direction for believers.
John Alexander Dowie
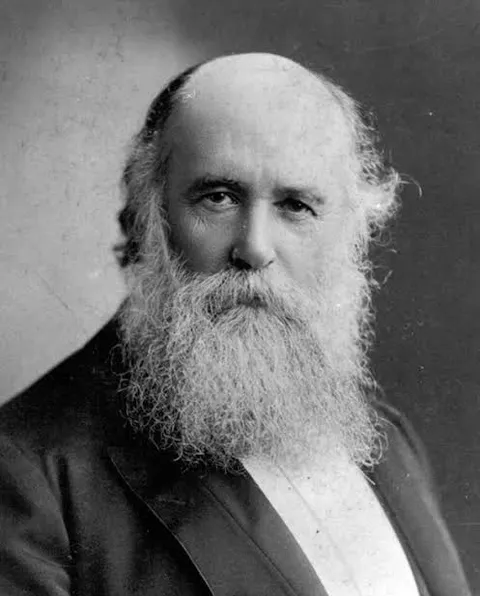 By John Alexander Dowie (1847 – 1907)
I sat in my study in the parsonage of the Congregational Church at Newtown, a suburb of the beautiful city of Sydney, Australia. My heart was very heavy, for I had visited the sick and dying beds of more than thirty of my flock, and I had cast the dust to its kindred dust into more than forty graves within a few weeks. Where, oh where, was He Who used to heal His suffering children? No prayer for healing seemed to reach His ear, and yet I knew His hand had not been shortened. Still it did not save from death even those for whom there was so much in life to live for God and others. Strong men, fathers, good citizens, and more than all, true Christians sickened with a putrid fever, suffered nameless agonies, passed into delirium, sometimes with convulsions, and then died.
Oh, what aching voids were left in many a widowed or orphaned heart. There were many homes where, one by one, the little children, the youths and the maidens lay stricken, and after a hard struggle with the foul disease, they too, lay cold and dead. It seemed sometimes as if I could almost hear the triumphant mockery of evil ringing in my ear whilst I spoke to the bereaved ones the words of Christian hope and consolation. Disease, the foul offspring of its father, Satan, and its mother Sin, was defiling and destroying the earthly temples of God’s children and there was no deliverance.
There I sat with sorrow-bowed head for my afflicted people, until the bitter tears came to relieve my burning heart. Then I prayed for some message, and oh, how I longed to hear some words from Him Who wept and sorrowed for the suffering long ago, a Man of Sorrows and Sympathies. The words of the Holy Ghost inspired In Acts 10:38, stood before me all radiant with light, revealing Satan as the Defiler, and Christ as the Healer. My tears were wiped away, my heart strong, I saw the way of healing, and the door thereto was opened wide, so I said, “God help me now to preach the Word to all the dying around, and tell them how Satan still defiles, and Jesus still delivers, for He is just the same today.”
A loud ring and several raps at the outer door, a rush of feet, and there at my door stood two panting messengers who said, “Oh, come at once, Mary is dying; come and pray. “With just a feeling as a shepherd has who hears that his sheep are being torn from the fold by a cruel wolf, I rushed from my house, ran without my hat down the street, and entered the room of the dying maiden. There she lay groaning and grinding her clenched teeth in the agony of the conflict with the destroyer. The white froth, mingled with her blood, oozing from her pale and distorted mouth. I looked at her and then my anger burned. “Oh,” I thought, “for some sharp sword of heavenly temper keen to slay this cruel foe who is strangling that lovely maiden like an invisible serpent, tightening his deadly coils for a final victory.”
In a strange way, It came to pass; I found the sword I needed was in my hands, and in my hand I hold it still and never will I lay It down. The doctor, a good Christian man, was quietly walking up and down the room, sharing the mother’s pain and grief. Presently he stood at my side and said, “Sir, are not God’s ways mysterious?” Instantly the sword was flashed in my hand, the Spirit’s sword, the Word of God. “God’s way?!” I said, pointing to the scene of conflict, “How dare you call that God’s way of bringing His children home from earth to Heaven? No sir, that is the devil’s work and it is time we called on Him Who came to destroy the work of the devil, to slay that deadly foul destroyer, and to save this child. Can you pray, Doctor, can you pray the prayer of faith that saves the sick?” At once, offended at my words, my friend was changed, and saying,” You are too much excited, sir, it is best to say ‘God’s will be done,’” and he left the room.
Excited?! The word was quite inadequate for I was almost frenzied with divinely imparted anger and hatred of that foul destroyer, disease, which was doing Satan’s will. “It is not so,” I exclaimed, “no will of God sends such cruelty, and I shall never say ‘God’s will be done’ to Satan’s works, which God’s own Son came to destroy, and this is one of them.” Oh, how the Word of God was burning in my heart: “Jesus of Nazareth went about doing good, and healing all that were oppressed of the devil; for God was with Him.” And was not God with me? And was not Jesus there and all His promises true? I felt that it was even so, and turning to the mother I inquired,” Why did you send for me?” To which she answered, “Do pray, oh pray for her that God may raise her up.” So we prayed.
What did I say? It may be that I cannot recall the words without mistake, but words are in themselves of small importance. The prayer of faith may be a voiceless prayer, a simple heartfelt look of confidence into the face of Christ. At such moment, words are few, but they mean much, for God is looking at the heart. Still, I can remember much of that prayer unto this day, and asking God to aid, I will attempt to recall it. I cried, “Our Father, help! and Holy Spirit, teach me how to pray. Plead Thou for us, oh, Jesus, Savior, Healer, Friend, our Advocate with God the Father. Hear and heal, Eternal One! From all disease and death, deliver this sweet child of yours. I rest upon the Word. We claim the promise now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord that heals thee.’ Then heal her now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord, I change not.’ Unchanging God, then prove Yourself the healer now. The Word is true. ‘These signs shall follow them that believe in My Name, they shall lay hands on the sick, and they shall recover.’ And I believe and I lay hands in Jesus’ Name on her and claim this promise now. Your Word is true. ‘The prayer of faith shall save the sick. Trusting in You alone. I cry. Oh, save her now, for Jesus’ sake. Amen!”
Then, the maid lay in sleep so deep and sweet that the mother asked in a low whisper, “Is she dead?” “No,” I answered, in a whisper lower still. “Mary will live; the fever is gone. She is perfectly well and sleeping as an infant sleeps.” I was smoothing the long dark hair from her now peaceful brow, and feeling the steady pulsation of her heart and cool moist hands. I saw that Christ had heard, and that once more, as long ago in Peter’s house, “He touched her and the fever left her.” Turning to the nurse, I said, “Get me at once, please, a cup of cocoa and several slices of bread and butter.” Beside the sleeping maid we sat quietly and almost silently until the nurse returned, and then I bent over her and snapping my fingers called, “Mary!”
Instantly she woke, smiled and said, “Oh, sir, when did you come? I have slept so long;” then stretching her arms out to meet her mother’s embrace, she said, “Mother, I feel so well.” “And hungry, too?” I asked, pouring some of the cocoa in a saucer and offering it to her when cooled by my breath. “Yes, hungry too,” she answered with a little laugh, and drank and ate again, and yet again until all was gone. In a few minutes, she fell asleep, breathing easily and softly. Quietly thanking God. We left her bed and went to the next room where her brother and sister also lay sick of the same fever. With these two, we prayed and they were healed too. The following day all three were well and in a week or so they brought me a little letter and a gift of gold, two sleeve links with my monogram, which I wore for many years. As I went away from the home where Christ as the Healer had been victorious, I could not but have somewhat in my heart of the triumphant song that rang through Heaven, and yet I was not a little amazed at my own strange doings, and still more at my discovery that He is just the same today.
Excerpt from the Sermons of John Alexander Dowie Champions of Faith by Gordon Lindsay
By John Alexander Dowie (1847 – 1907)
I sat in my study in the parsonage of the Congregational Church at Newtown, a suburb of the beautiful city of Sydney, Australia. My heart was very heavy, for I had visited the sick and dying beds of more than thirty of my flock, and I had cast the dust to its kindred dust into more than forty graves within a few weeks. Where, oh where, was He Who used to heal His suffering children? No prayer for healing seemed to reach His ear, and yet I knew His hand had not been shortened. Still it did not save from death even those for whom there was so much in life to live for God and others. Strong men, fathers, good citizens, and more than all, true Christians sickened with a putrid fever, suffered nameless agonies, passed into delirium, sometimes with convulsions, and then died.
Oh, what aching voids were left in many a widowed or orphaned heart. There were many homes where, one by one, the little children, the youths and the maidens lay stricken, and after a hard struggle with the foul disease, they too, lay cold and dead. It seemed sometimes as if I could almost hear the triumphant mockery of evil ringing in my ear whilst I spoke to the bereaved ones the words of Christian hope and consolation. Disease, the foul offspring of its father, Satan, and its mother Sin, was defiling and destroying the earthly temples of God’s children and there was no deliverance.
There I sat with sorrow-bowed head for my afflicted people, until the bitter tears came to relieve my burning heart. Then I prayed for some message, and oh, how I longed to hear some words from Him Who wept and sorrowed for the suffering long ago, a Man of Sorrows and Sympathies. The words of the Holy Ghost inspired In Acts 10:38, stood before me all radiant with light, revealing Satan as the Defiler, and Christ as the Healer. My tears were wiped away, my heart strong, I saw the way of healing, and the door thereto was opened wide, so I said, “God help me now to preach the Word to all the dying around, and tell them how Satan still defiles, and Jesus still delivers, for He is just the same today.”
A loud ring and several raps at the outer door, a rush of feet, and there at my door stood two panting messengers who said, “Oh, come at once, Mary is dying; come and pray. “With just a feeling as a shepherd has who hears that his sheep are being torn from the fold by a cruel wolf, I rushed from my house, ran without my hat down the street, and entered the room of the dying maiden. There she lay groaning and grinding her clenched teeth in the agony of the conflict with the destroyer. The white froth, mingled with her blood, oozing from her pale and distorted mouth. I looked at her and then my anger burned. “Oh,” I thought, “for some sharp sword of heavenly temper keen to slay this cruel foe who is strangling that lovely maiden like an invisible serpent, tightening his deadly coils for a final victory.”
In a strange way, It came to pass; I found the sword I needed was in my hands, and in my hand I hold it still and never will I lay It down. The doctor, a good Christian man, was quietly walking up and down the room, sharing the mother’s pain and grief. Presently he stood at my side and said, “Sir, are not God’s ways mysterious?” Instantly the sword was flashed in my hand, the Spirit’s sword, the Word of God. “God’s way?!” I said, pointing to the scene of conflict, “How dare you call that God’s way of bringing His children home from earth to Heaven? No sir, that is the devil’s work and it is time we called on Him Who came to destroy the work of the devil, to slay that deadly foul destroyer, and to save this child. Can you pray, Doctor, can you pray the prayer of faith that saves the sick?” At once, offended at my words, my friend was changed, and saying,” You are too much excited, sir, it is best to say ‘God’s will be done,’” and he left the room.
Excited?! The word was quite inadequate for I was almost frenzied with divinely imparted anger and hatred of that foul destroyer, disease, which was doing Satan’s will. “It is not so,” I exclaimed, “no will of God sends such cruelty, and I shall never say ‘God’s will be done’ to Satan’s works, which God’s own Son came to destroy, and this is one of them.” Oh, how the Word of God was burning in my heart: “Jesus of Nazareth went about doing good, and healing all that were oppressed of the devil; for God was with Him.” And was not God with me? And was not Jesus there and all His promises true? I felt that it was even so, and turning to the mother I inquired,” Why did you send for me?” To which she answered, “Do pray, oh pray for her that God may raise her up.” So we prayed.
What did I say? It may be that I cannot recall the words without mistake, but words are in themselves of small importance. The prayer of faith may be a voiceless prayer, a simple heartfelt look of confidence into the face of Christ. At such moment, words are few, but they mean much, for God is looking at the heart. Still, I can remember much of that prayer unto this day, and asking God to aid, I will attempt to recall it. I cried, “Our Father, help! and Holy Spirit, teach me how to pray. Plead Thou for us, oh, Jesus, Savior, Healer, Friend, our Advocate with God the Father. Hear and heal, Eternal One! From all disease and death, deliver this sweet child of yours. I rest upon the Word. We claim the promise now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord that heals thee.’ Then heal her now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord, I change not.’ Unchanging God, then prove Yourself the healer now. The Word is true. ‘These signs shall follow them that believe in My Name, they shall lay hands on the sick, and they shall recover.’ And I believe and I lay hands in Jesus’ Name on her and claim this promise now. Your Word is true. ‘The prayer of faith shall save the sick. Trusting in You alone. I cry. Oh, save her now, for Jesus’ sake. Amen!”
Then, the maid lay in sleep so deep and sweet that the mother asked in a low whisper, “Is she dead?” “No,” I answered, in a whisper lower still. “Mary will live; the fever is gone. She is perfectly well and sleeping as an infant sleeps.” I was smoothing the long dark hair from her now peaceful brow, and feeling the steady pulsation of her heart and cool moist hands. I saw that Christ had heard, and that once more, as long ago in Peter’s house, “He touched her and the fever left her.” Turning to the nurse, I said, “Get me at once, please, a cup of cocoa and several slices of bread and butter.” Beside the sleeping maid we sat quietly and almost silently until the nurse returned, and then I bent over her and snapping my fingers called, “Mary!”
Instantly she woke, smiled and said, “Oh, sir, when did you come? I have slept so long;” then stretching her arms out to meet her mother’s embrace, she said, “Mother, I feel so well.” “And hungry, too?” I asked, pouring some of the cocoa in a saucer and offering it to her when cooled by my breath. “Yes, hungry too,” she answered with a little laugh, and drank and ate again, and yet again until all was gone. In a few minutes, she fell asleep, breathing easily and softly. Quietly thanking God. We left her bed and went to the next room where her brother and sister also lay sick of the same fever. With these two, we prayed and they were healed too. The following day all three were well and in a week or so they brought me a little letter and a gift of gold, two sleeve links with my monogram, which I wore for many years. As I went away from the home where Christ as the Healer had been victorious, I could not but have somewhat in my heart of the triumphant song that rang through Heaven, and yet I was not a little amazed at my own strange doings, and still more at my discovery that He is just the same today.
Excerpt from the Sermons of John Alexander Dowie Champions of Faith by Gordon Lindsay
What Does It Mean to Be Real
Nobody likes a fake. Even in our airbrush culture, we despise counterfeits and crave authenticity. Everyone wants to be real. But what does it mean to be real? No one really knows. Or so it seems. Try an experiment. Listen to people talk about what it means to be a Christian. Do you know what you will hear? Lots of competing answers and plenty of confusion. Perhaps you recall when 2012 presidential hopeful, Senator Rick Santorum, claimed that President Barack Obama’s policies were based on “a different theology.” Reporters, of course, pounced on this juicy piece of journalist red meat. “Did Senator Santorum,” they asked, “have the audacity, not of hope, but political incorrectness, to call into question the president’s claim to be a Christian?” When Senator Santorum was pressed, he gave a politically savvy response: “If the president says he’s a Christian, he’s a Christian.” End of story. Next question, please. His answer satisfied reporters, and thousands of others following the story. It was as if he said, “To profess faith is to possess faith.” And what could be less objectionable, or more American, than that? But one wonders what Jesus thinks of what Santorum said. More Than Mere Talk Is it enough simply to say we’re real, or should we be able to see we’re real? And if so, what should we see? Are there marks of authentic faith we should see in our lives, or in the lives of others? And what about the watching world? What should they see in the lives of real Christians? Now, more than a decade into the twenty-first century, the evangelical church faces huge challenges to its ministry and mission — radical pluralism, aggressive secularism, political polarization, skepticism about religion, revisionist sexual ethics, postmodern conceptions of truth. But perhaps the greatest threat to the church’s witness is one of our own making — an image problem. Many outside the church view Christians as unchristian in their attitudes and actions — bigoted, homophobic, hypocritical, materialistic, judgmental, self-serving, overly political. Several years ago, David Kinnaman and Gabe Lyons showed this in their book Unchristian , which landed like a bombshell on a happy-go-lucky evangelicalism, causing many of us to do some serious soul-searching. The evangelical church’s image problem doesn’t bode well for its future. In fact, the data suggests that evangelical Christianity is declining in North America. Despite the church’s best efforts to appeal to the disillusioned, we continue to see alarming trends. Droves of people, especially from younger generations, are leaving the church and don’t plan to return. This has driven some to even predict the end of evangelicalism (See David Fitch, The End of Evangelicalism? ). One True Soil The reasons for this discouraging state of affairs are complex, not cookie-cutter. But we know one thing is certain: When Christians are confused about what it means to be real, the spiritual decline of the church will follow. In our increasingly post-Christian culture, where confusion about what it means to be real abounds, and where distrust of organized religion has reached an all-time high, the church needs to get real . We must clarify for ourselves, and for a watching world, what it means to live a life of authentic faith. While Christians are confused about what it means to be real, Jesus is not. “Thus you will recognize them by their fruits,” he says (Matthew 7:20). You know you’re real if you bear fruit, he tells us. Fruit is the telltale sign of authentic faith because fruit doesn’t lie. “For no good tree bears bad fruit, nor again does a bad tree bear good fruit, for each tree is known by its own fruit. For figs are not gathered from thornbushes, nor are grapes picked from a bramble bush” (Luke 6:43–44). Jesus underscores this point in his famous parable about the sower (Matthew 13:1–23). The parable itself is straightforward. A farmer sows seed in a field, and the seed represents the good news of the kingdom. It is sown on four different kinds of soil, each representing a different response to the message of the kingdom. Simple enough, right? But here’s the punch line: Only one type of soil bears fruit. Counterfeits Exposed The seed sown on the first soil hardly gets started. Satan comes and snatches it away. But what’s even more troubling is the outcome of the seed sown on the second and third soils. Why? Because both respond positively to the message, at least initially. These seeds appear to take root and begin growing into something real. Yet as the story continues, we learn that neither seed bears fruit. Neither lasts to the end, and thus neither seed is real. Some of the seeds fail to develop roots, and they don’t persevere when life gets hard and their faith is tested. All we see from this seed is a burst of enthusiasm, but no staying power. Perhaps this is someone who got excited about fellowship or forgiveness, but lacked love for Christ. They only have the appearance of being real. Over time, their faith proved counterfeit. We assume the third seed had a similarly joyful response to the message. Yet this soon dissipates because of revived interest in the things of the world — a career promotion, a new vacation home, saving toward their 401(k) plan. These concerns choke any fledgling faith, and the person falls away. New People with New Lives Why does Jesus tell his disciples this sobering parable? Why such a blunt story about the distinction between authentic and inauthentic responses to his message? Evidently, Jesus doesn’t equate professing faith with possessing faith, as we so often do. Instead, he warns his disciples that only one things matters — bearing fruit Although provocative, I think Jesus’s point is simple. Real is something you can see. There is a visible difference between real and not-real Christians. It’s not enough to say you’re real; you should be able to see you’re real. Real faith is something you can see. Being real is more than regularly attending church, feeling good about God, or “accepting” Jesus as your Savior; it goes beyond being baptized, receiving Communion, reciting the creed, or joining in church membership. As important as these things are, being real runs deeper than these things. Real Christians are new creatures. Physically, they won’t look different than others, at least not in the way they dress or keep their hair. Yet real Christians are radically changed — they’ve experienced a new birth, received a new heart, and enjoy new desires. Which makes them altogether new people who live new lives. And it shows. If you’re real, it will reveal itself in your life. Real Christians bear the marks of authentic faith in ways that can be seen, heard, and felt. When you know what you’re looking for, you can see the marks of real in their lives — and in your own.

.mobi-480.webp)
