Others like standing on the promises Features >>

Restoring The Christian Family

Marriage On The Rock - God's Design For Your Dream Marriage

Finding Home - An Imperfect Path To Faith And Family
-160.webp)
Building Stronger Marriages And Families

I'm Married Now!

Keys For Marriage

101 Ways To Have 100% Success In Marriage
Wired For Intimacy
-160.webp)
Sheet Music (Uncovering The Secrets Of Sexual Intimacy In Marraige)

Celebrating Marriage
About the Book
"Standing On The Promises" is a Christian fiction novel by Susan Wales that follows the journey of three women who face challenges, heartbreak, and self-discovery while navigating their faith. As they lean on the promises of God, they find strength, healing, and redemption in the face of adversity.
Kathryn Kuhlman
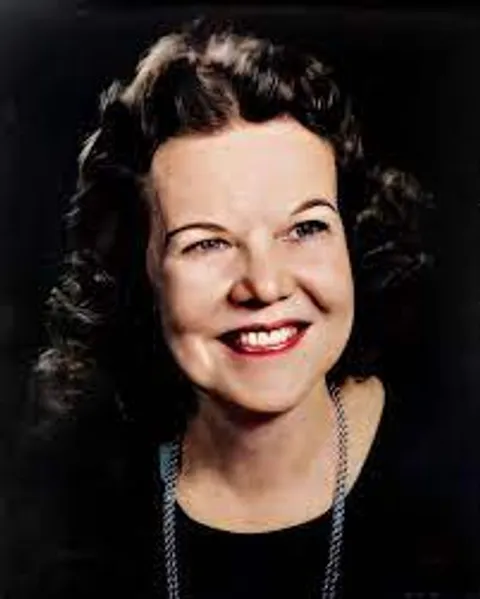 Kathryn Johanna Kuhlman was born on May 9, 1907, in Concordia, Missouri. Her parents were German and she was one of four children. Her mother was a harsh disciplinarian, who showed little love or affection. On the other hand, she had an extremely close and loving relationship with her father. She would describe, as a small child how, her father would come home from work and she would hang on his leg and cling to him. She often said that her relationship with God the Father was extremely real because of her relationship with her own father.
Kuhlman was converted, when she was 14, at an evangelistic meeting held in a small Methodist church. When she was 16 she graduated from high school, which only went to tenth grade in their town. He older sister Myrtle had married an itinerant evangelist, Everett B. Parrott. They spent their time traveling and asked that Kathryn could join them for the summer. Her parents agreed and she went to Oregon to help out. She worked with them, and often gave her testimony. When the summer was over she wanted to stay, and the couple agreed. She ended up working with them for five years.
The evangelistic team was made up of four people, Everette, Myrtle, Kathryn, and pianists named Helen Gulliford. In 1928 Everette missed a meeting in Boise, Idaho. Myrtle and Kathryn preached to cover for Everette. The pastor of the church encouraged Kathryn to step out on her own. Helen agreed to join her. Her first sermon was in a run-down pool hall in Boise, Idaho. The team covered Idaho, Utah, and Colorado for the following five years. In 1933 they moved into Pueblo, Colorado. They set up in an abandoned Montgomery Ward warehouse. They stayed there for six months.
Denver, being a much bigger city, was the next stop. They moved several times but ended up in a paper company's warehouse, which they named the Kuhlman Revival Tabernacle. Then in 1935 they moved once more to an abandoned truck garage they named the Denver Revival Tabernacle. Kathryn was seeing a lot of success in Denver. The church grew to about 2000 members. She began a radio show called "Smiling Through" and invited speakers from all over the country. One of them was Phil Kerr who taught on divine healing. In 1935 another invited evangelist was Burroughs Waltrip.
Waltrip was bad news for Kuhlman. He was a charismatic, handsome man several years older than she was. There was an immediate attraction, and one family claims to have seen the couple embracing in 1935, but he was married and had two children. Waltrip left Denver and went home to Austin, Texas, but the relationship simmered between Kuhlman and Waltrip. In 1937 he was invited back to Denver to take the pulpit for two months. Shortly after he divorced his wife and abandoned his two sons. He then spread the story that his wife had left him. He moved to Mason City, Iowa, where he told everyone he was single, and started a new ministry. Waltrip raised pledges of $70,000 to build a ministry building called Radio Chapel. It was state of the art with a disappearing pulpit and an art deco style. He appeared to be a successful and dynamic preacher.
There was an ongoing relationship between Kuhlman and Waltrip, and they married in September 1938. Kuhlman was naive about the consequences of her choices and the marriage was a disaster. She announced to her church that she and Waltrip were married and they would go between Denver and Mason City preaching at their two churches. Most of the people in her congregation left due to her relationship with Waltrip. She gave up her church in Denver, lost some of her closest associates, and moved to Mason City. Waltrip's success turned out to be a pipe dream as well. The Radio Chapel was completed in June of 1938. By October 1938 Waltrip could not meet his debts. In December Waltrip was demanding a higher salary, even with the shortfall in income. His Board of Directors quit and left him to deal with the finances. His solution was not to pay the mortgage or debts on the Chapel. Radio Chapel went into bankruptcy. Waltrip's last sermon was in May 1939. The Waltrips were on their own. Kathryn's happy vision of she and her husband flying back and forth between Denver and Mason City with a successful preaching careers was utterly demolished.
The next few years were very hard for the couple. They embarked on the road as traveling evangelists, primarily staying in the Midwest. They were not accepted in many places due to their marriage history. Initial advertisements listed Waltrip as the primary evangelist. Then occasionally Mrs. Waltrip was also mentioned. By the early 1940s Kathryn Kuhlman Waltrip was given equal billing. Finally by the mid-1940s Kathryn was using only Kathryn Kuhlman in meetings where she was the primary speaker. In 1944 Kuhlman went on an evangelistic tour on the east coast without Waltrip. It may have been a conscious decision to leave him, or she may also have taken the opportunity to reassess her life. It appears to have been more gradual as Waltrip wrote about them as a couple as late as 1946. Kuhlman never returned to Waltrip and they eventually divorced in 1947. She left her marriage behind and from then on acted as if it never existed in the first place.
In 1946 Kuhlman was asked to speak in Franklin, Pennsylvania. She was well received and decided to stay in the area. Kuhlman began preaching on radio broadcasts in Oil City, Pennsylvania. These became so popular they were picked up in Pittsburgh, and she was preaching throughout the area. She began to preach about the healing power of God. In 1947 a woman was healed of a tumor while listening to Kuhlman preach. Several Sundays later a man was also healed while she was teaching on the Holy Spirit. She was now convinced of God's healing work. One important thing to note is the context and timing of this breakout period in Kuhlman's life. 1947 was the beginning of the Healing Revival (sometimes referred to as the Latter Rain Revival) that would last for the next 10 years. What was happening in Kuhlman's meetings was breaking out across the United States. It was in this time frame that the Voice of Healing Ministry was established and men like William Branham, Oral Roberts, A.A. Allen and many others were propelled onto the public stage. Kuhlman was not associated with those groups, but stepped into the flow of what God's Spirit was doing across the nation and the world.
In 1948 Kuhlman held a series of meetings at Carnegie Hall in Pittsburgh. She eventually moved to Pittsburgh in 1950, and continued to hold meetings at Carnegie Hall until 1971. She was used by God to bring the charismatic message to many denominational churches, including the Catholic Church. (She received a lot of criticism over this and was accused of being a closet Catholic.) These were her best known years. Her style was flamboyant. She would hold her famous miracle services and the auditorium was filled to capacity every time. She was on radio and television shows. She was ordained in 1968 by the Evangelical Church Alliance. Hundreds of people were healed in her meetings, and even while listening to her on the radio or television. People she prayed for would often be hit with the power of God and be "slain in the Spirit." Kuhlman never claimed that she was the healer. She always pointed people to Jesus as their healer.
Kuhlman had been diagnosed with a heart problem in 1955. She kept a very busy schedule and overworked herself, especially in the 1970's. She traveled back and forth from Pittsburgh to Los Angeles frequently, as well as taking trips around the world. Her heart was enlarged and Kuhlman died on February 20, 1976, in Tulsa, following open-heart surgery. Videos of some of her services are still available and continue to be popular today.
Kathryn Johanna Kuhlman was born on May 9, 1907, in Concordia, Missouri. Her parents were German and she was one of four children. Her mother was a harsh disciplinarian, who showed little love or affection. On the other hand, she had an extremely close and loving relationship with her father. She would describe, as a small child how, her father would come home from work and she would hang on his leg and cling to him. She often said that her relationship with God the Father was extremely real because of her relationship with her own father.
Kuhlman was converted, when she was 14, at an evangelistic meeting held in a small Methodist church. When she was 16 she graduated from high school, which only went to tenth grade in their town. He older sister Myrtle had married an itinerant evangelist, Everett B. Parrott. They spent their time traveling and asked that Kathryn could join them for the summer. Her parents agreed and she went to Oregon to help out. She worked with them, and often gave her testimony. When the summer was over she wanted to stay, and the couple agreed. She ended up working with them for five years.
The evangelistic team was made up of four people, Everette, Myrtle, Kathryn, and pianists named Helen Gulliford. In 1928 Everette missed a meeting in Boise, Idaho. Myrtle and Kathryn preached to cover for Everette. The pastor of the church encouraged Kathryn to step out on her own. Helen agreed to join her. Her first sermon was in a run-down pool hall in Boise, Idaho. The team covered Idaho, Utah, and Colorado for the following five years. In 1933 they moved into Pueblo, Colorado. They set up in an abandoned Montgomery Ward warehouse. They stayed there for six months.
Denver, being a much bigger city, was the next stop. They moved several times but ended up in a paper company's warehouse, which they named the Kuhlman Revival Tabernacle. Then in 1935 they moved once more to an abandoned truck garage they named the Denver Revival Tabernacle. Kathryn was seeing a lot of success in Denver. The church grew to about 2000 members. She began a radio show called "Smiling Through" and invited speakers from all over the country. One of them was Phil Kerr who taught on divine healing. In 1935 another invited evangelist was Burroughs Waltrip.
Waltrip was bad news for Kuhlman. He was a charismatic, handsome man several years older than she was. There was an immediate attraction, and one family claims to have seen the couple embracing in 1935, but he was married and had two children. Waltrip left Denver and went home to Austin, Texas, but the relationship simmered between Kuhlman and Waltrip. In 1937 he was invited back to Denver to take the pulpit for two months. Shortly after he divorced his wife and abandoned his two sons. He then spread the story that his wife had left him. He moved to Mason City, Iowa, where he told everyone he was single, and started a new ministry. Waltrip raised pledges of $70,000 to build a ministry building called Radio Chapel. It was state of the art with a disappearing pulpit and an art deco style. He appeared to be a successful and dynamic preacher.
There was an ongoing relationship between Kuhlman and Waltrip, and they married in September 1938. Kuhlman was naive about the consequences of her choices and the marriage was a disaster. She announced to her church that she and Waltrip were married and they would go between Denver and Mason City preaching at their two churches. Most of the people in her congregation left due to her relationship with Waltrip. She gave up her church in Denver, lost some of her closest associates, and moved to Mason City. Waltrip's success turned out to be a pipe dream as well. The Radio Chapel was completed in June of 1938. By October 1938 Waltrip could not meet his debts. In December Waltrip was demanding a higher salary, even with the shortfall in income. His Board of Directors quit and left him to deal with the finances. His solution was not to pay the mortgage or debts on the Chapel. Radio Chapel went into bankruptcy. Waltrip's last sermon was in May 1939. The Waltrips were on their own. Kathryn's happy vision of she and her husband flying back and forth between Denver and Mason City with a successful preaching careers was utterly demolished.
The next few years were very hard for the couple. They embarked on the road as traveling evangelists, primarily staying in the Midwest. They were not accepted in many places due to their marriage history. Initial advertisements listed Waltrip as the primary evangelist. Then occasionally Mrs. Waltrip was also mentioned. By the early 1940s Kathryn Kuhlman Waltrip was given equal billing. Finally by the mid-1940s Kathryn was using only Kathryn Kuhlman in meetings where she was the primary speaker. In 1944 Kuhlman went on an evangelistic tour on the east coast without Waltrip. It may have been a conscious decision to leave him, or she may also have taken the opportunity to reassess her life. It appears to have been more gradual as Waltrip wrote about them as a couple as late as 1946. Kuhlman never returned to Waltrip and they eventually divorced in 1947. She left her marriage behind and from then on acted as if it never existed in the first place.
In 1946 Kuhlman was asked to speak in Franklin, Pennsylvania. She was well received and decided to stay in the area. Kuhlman began preaching on radio broadcasts in Oil City, Pennsylvania. These became so popular they were picked up in Pittsburgh, and she was preaching throughout the area. She began to preach about the healing power of God. In 1947 a woman was healed of a tumor while listening to Kuhlman preach. Several Sundays later a man was also healed while she was teaching on the Holy Spirit. She was now convinced of God's healing work. One important thing to note is the context and timing of this breakout period in Kuhlman's life. 1947 was the beginning of the Healing Revival (sometimes referred to as the Latter Rain Revival) that would last for the next 10 years. What was happening in Kuhlman's meetings was breaking out across the United States. It was in this time frame that the Voice of Healing Ministry was established and men like William Branham, Oral Roberts, A.A. Allen and many others were propelled onto the public stage. Kuhlman was not associated with those groups, but stepped into the flow of what God's Spirit was doing across the nation and the world.
In 1948 Kuhlman held a series of meetings at Carnegie Hall in Pittsburgh. She eventually moved to Pittsburgh in 1950, and continued to hold meetings at Carnegie Hall until 1971. She was used by God to bring the charismatic message to many denominational churches, including the Catholic Church. (She received a lot of criticism over this and was accused of being a closet Catholic.) These were her best known years. Her style was flamboyant. She would hold her famous miracle services and the auditorium was filled to capacity every time. She was on radio and television shows. She was ordained in 1968 by the Evangelical Church Alliance. Hundreds of people were healed in her meetings, and even while listening to her on the radio or television. People she prayed for would often be hit with the power of God and be "slain in the Spirit." Kuhlman never claimed that she was the healer. She always pointed people to Jesus as their healer.
Kuhlman had been diagnosed with a heart problem in 1955. She kept a very busy schedule and overworked herself, especially in the 1970's. She traveled back and forth from Pittsburgh to Los Angeles frequently, as well as taking trips around the world. Her heart was enlarged and Kuhlman died on February 20, 1976, in Tulsa, following open-heart surgery. Videos of some of her services are still available and continue to be popular today.
disowned for jesus - what i lost and found in christ
When I left Islam to follow Jesus, I didn’t know what it would cost me. I hadn’t realized what it would take to deny myself, lay my life down, and take up my cross (Matthew 16:24). I wasn’t aware that even the precious relationships of my family should not come between me and following Christ — that I should even hate my family compared to my love for Jesus (Luke 14:26). But God taught me that if I do take up my cross and lay down my life, then I’ll find my life. Over time, I have come to experience this truth. My life of following Jesus has not been the life I envisioned for myself, but it has become the life I want: a life used for the glory of God as I grow in the knowledge of Christ and make him known to others. That’s what I discovered when I was forced to choose between Jesus and my father. From Iran to Texas I was born in Houston and grew up in a devout Muslim home. My dad was very involved in the Iranian Muslim community. Growing up, I was taught the five pillars of Islam and that if I did them to the best of my ability, then maybe I’d get to heaven. When I was two years old, my family moved to Iran, where my parents are from. But at age six, the Islamic Revolution of the late ’70s hit that country. My father, who was a doctor, had the means to get us out of the country, so our family moved back to Houston. I spoke Farsi, not English, and so God, in his incredible plan, provided a Christian lady who tutored me, teaching me the English language every day by reading books to me. In the second grade, she said to me, “Afshin, I want to give you the most important book that you’ll ever read in life.” As she handed me a small New Testament, she told me that I would not completely understand it now, but asked me to promise to hold onto it until I was older. She gave me that Bible during the Iran hostage crisis, a time during which my family and other Iranians in America were ostracized and hated by many. This lady, however, earned the right to be heard by the way that she loved me, showed me the love of Christ, and poured her life into me. Because the Bible came from her, I believed it was important, and held onto that New Testament. She had planted a seed in my life in the second grade that wouldn’t come to fruition until ten years later. Leaving Islam As a senior in high school, I used the Lord’s name in vain while playing basketball. A guy on the court walked up to me and said, “Hey, that Jesus whose name you just said — he’s my God.” As a Muslim, I’d been taught that Jesus was a prophet, so I thought the guy was nuts. A few days later, while watching TV, I stumbled onto a historical documentary on the life of Jesus, where I heard, “Some worship Jesus as God, and they’re called Christians.” My mind went back to the words of the guy on the basketball court, and the Lord reminded me of the Bible that I’d received ten years earlier. That afternoon, I found that small New Testament at the bottom of my closet and began to read in Matthew. Every day, I’d read under the covers in my bed with a flashlight so that my parents wouldn’t walk in and see what I was doing. Meanwhile, at my high school, a Christian student sat across the table from me at lunch and told me about Jesus. I’d debate against him each day, and then at night I’d go home to read more about his Jesus. One day, I got to the book of Romans, and the third chapter completely changed my life. I read about a righteousness that comes apart from the law, apart from what I do for God. I read that this righteousness comes as a gift to be received by faith. I was struck by Romans 3:22, which says that this righteousness comes to all who believe. I thought I was born a Muslim and would always be a Muslim, but that verse said that this righteousness was for anyone who believes, of any ethnicity. A couple weeks later, a guy invited me to an evangelistic crusade (always an interesting word for a Muslim!), where I heard the gospel proclaimed and came to faith in Christ. As an aside: I’m often asked what form of evangelism I believe to be most effective. God used evangelism in a variety of forms in my life. He used a teacher loving and tutoring a kid, a guy sharing one-on-one in a cafeteria, a guy speaking up for the name of Christ on a basketball court, an invitation to an evangelistic event, and the preaching of the gospel in a corporate setting. I believe in each of these forms of evangelism because God used each one of them in my own life. Disowned I made my commitment to Christ public at that evangelistic crusade, but driving home from the event is when it hit me: “What am I going to tell my family? What am I going to tell my father?” My father had always been the most important person in my life, the guy I’d always looked up to. I’m ashamed to say that I decided to hide my newfound faith from him and the rest of my family. I would sneak out to go to church, intercept mail from the church I was attending, and hide my Bible. Finally, one day my dad found out. He’d seen my Bible, and he’d also seen other evidences in my life. He sat me down and said, “Son, what’s going on? There’s something different about you.” I said, “Dad, I’m a Christian.” He said, “No, you’re not, young man. you’re a Muslim and you’ll always be a Muslim.” I said, “Dad, the Bible says that if I trust in Christ alone for my salvation, then I’m a Christian — and I do.” My dad said, “Afshin, if you’re going to be a Christian, then you can no longer be my son.” Everything in my flesh wanted to say, “Forget it. I’ll be a Muslim.” I didn’t want to lose the relationship with my dad. So even I was surprised when I opened my mouth and said, “Dad, if I have to choose between you and Jesus, then I choose Jesus. And if I have to choose between my earthly father and my heavenly Father, then I choose my heavenly Father.” My father disowned me on the spot. Not Peace, but a Sword I went upstairs to my room, and in the defining moment of my life, said, “God, how could you do this to me? Jesus, if you’re real, how could you take my dad away from me?” The Lord led me to where Jesus says, “Everyone who acknowledges me before men, I also will acknowledge before my Father who is in heaven, but whoever denies me before men, I also will deny before my Father who is in heaven. Do not think that I have come to bring peace to the earth. I have not come to bring peace, but a sword. For I have come to set a man against his father.” (Matthew 10:32–35) I read this just moments after my dad disowned me, and thought, Whoa! This just happened for me! Jesus goes on to say, “I have come to set . . . a daughter against her mother, and a daughter-in-law against her mother-in-law. And a person’s enemies will be those of his own household. Whoever loves father or mother more than me is not worthy of me, and whoever loves son or daughter more than me is not worthy of me. And whoever does not take his cross and follow me is not worthy of me. Whoever finds his life will lose it, and whoever loses his life for my sake will find it.” (Matthew 10:35–39) That’s when I first understood what it means to be a follower of Christ. Life Lost and Found I had to lose my father to follow Christ. But I learned firsthand that when you lose your life, you find it. God gave me a roommate in college who was also a former Muslim and was also disowned by his father. After college, God led me to seminary. He provided a businessman in Dallas who paid for my entire seminary degree and a church internship, which eventually led to a position as a college pastor. God gave me a fifteen-year speaking ministry where I traveled all over the United States, preached the gospel, and saw Muslims come to faith in Christ. I have partnered with a ministry that reaches into Iran with the gospel, and have had the privilege of training and equipping Iranian pastors, helping to spread the gospel in the same nation from which my family came. I now pastor a church in Frisco, Texas, where I get to weekly remind our people to count the cost of following Christ. As a result, we have grown, planted three churches, and sent out several missionaries around the world. Finally, I am thrilled to say that my relationship with my dad has been restored, and I continue to pray for his salvation daily. What Has Jesus Cost You? I’m passionate for people to know that there’s a cost to following Jesus. What is it costing you to follow him? It might be that the thing you’re holding onto is the thing that’s keeping you from living for his glory. For me, it was my dad. For you, it might be something else. There is a huge difference between being a follower of Christ and merely giving mental assent to the truths about Jesus. The call of Christ isn’t simply “Believe the right things about me” but “Follow me.” And following Jesus is defined by losing your life. It is laying down your dreams, your pursuits, your idols to grab ahold of the greatest treasure in life: Jesus. When we lose our lives, God will leverage our lives for his glory and for others to know Jesus. There is no greater joy and fulfillment in life than this.



