-480.webp)
Quiet Time (School Of The Word) Order Printed Copy
- Author: Dag Heward Mills
- Size: 841KB | 65 pages
- |
Others like quiet time (school of the word) Features >>

The Greatest Salesman In The World - Part 2

Experiencing The Words Of Jesus

The Finest Of The Wheat

The Sermon On The Mount

The Sermon On The Mount

The Shelter Of The Most High

Smith Wigglesworth On The Power Of Scripture

Letters Of Samuel Rutherford - With A Sketch Of His Life

Take Time To Be Holy: 365 Daily Inspirations To Bring You Closer To God

40 Days In The Word
About the Book
"Quiet Time (School of the Word)" by Dag Heward Mills is a practical guide to establishing and maintaining a daily quiet time with God. The book emphasizes the importance of spending time in prayer, meditation, and studying the Bible in order to grow spiritually and deepen one's relationship with God. It offers practical tips and insights on how to make the most of quiet time and draw closer to God through regular, intentional time spent in reflection and communion with Him.
Kathryn Kuhlman
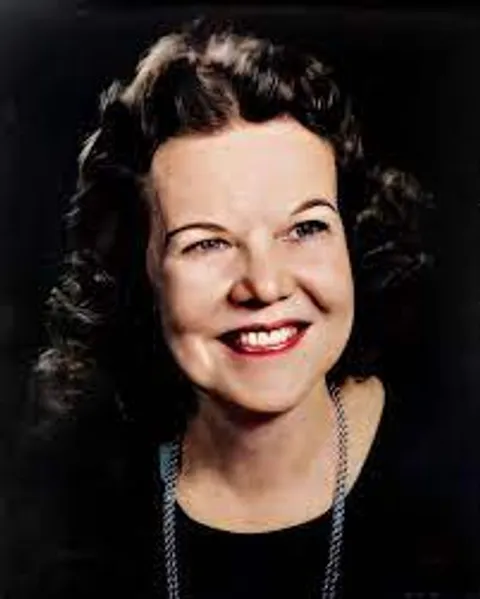 Kathryn Johanna Kuhlman was born on May 9, 1907, in Concordia, Missouri. Her parents were German and she was one of four children. Her mother was a harsh disciplinarian, who showed little love or affection. On the other hand, she had an extremely close and loving relationship with her father. She would describe, as a small child how, her father would come home from work and she would hang on his leg and cling to him. She often said that her relationship with God the Father was extremely real because of her relationship with her own father.
Kuhlman was converted, when she was 14, at an evangelistic meeting held in a small Methodist church. When she was 16 she graduated from high school, which only went to tenth grade in their town. He older sister Myrtle had married an itinerant evangelist, Everett B. Parrott. They spent their time traveling and asked that Kathryn could join them for the summer. Her parents agreed and she went to Oregon to help out. She worked with them, and often gave her testimony. When the summer was over she wanted to stay, and the couple agreed. She ended up working with them for five years.
The evangelistic team was made up of four people, Everette, Myrtle, Kathryn, and pianists named Helen Gulliford. In 1928 Everette missed a meeting in Boise, Idaho. Myrtle and Kathryn preached to cover for Everette. The pastor of the church encouraged Kathryn to step out on her own. Helen agreed to join her. Her first sermon was in a run-down pool hall in Boise, Idaho. The team covered Idaho, Utah, and Colorado for the following five years. In 1933 they moved into Pueblo, Colorado. They set up in an abandoned Montgomery Ward warehouse. They stayed there for six months.
Denver, being a much bigger city, was the next stop. They moved several times but ended up in a paper company's warehouse, which they named the Kuhlman Revival Tabernacle. Then in 1935 they moved once more to an abandoned truck garage they named the Denver Revival Tabernacle. Kathryn was seeing a lot of success in Denver. The church grew to about 2000 members. She began a radio show called "Smiling Through" and invited speakers from all over the country. One of them was Phil Kerr who taught on divine healing. In 1935 another invited evangelist was Burroughs Waltrip.
Waltrip was bad news for Kuhlman. He was a charismatic, handsome man several years older than she was. There was an immediate attraction, and one family claims to have seen the couple embracing in 1935, but he was married and had two children. Waltrip left Denver and went home to Austin, Texas, but the relationship simmered between Kuhlman and Waltrip. In 1937 he was invited back to Denver to take the pulpit for two months. Shortly after he divorced his wife and abandoned his two sons. He then spread the story that his wife had left him. He moved to Mason City, Iowa, where he told everyone he was single, and started a new ministry. Waltrip raised pledges of $70,000 to build a ministry building called Radio Chapel. It was state of the art with a disappearing pulpit and an art deco style. He appeared to be a successful and dynamic preacher.
There was an ongoing relationship between Kuhlman and Waltrip, and they married in September 1938. Kuhlman was naive about the consequences of her choices and the marriage was a disaster. She announced to her church that she and Waltrip were married and they would go between Denver and Mason City preaching at their two churches. Most of the people in her congregation left due to her relationship with Waltrip. She gave up her church in Denver, lost some of her closest associates, and moved to Mason City. Waltrip's success turned out to be a pipe dream as well. The Radio Chapel was completed in June of 1938. By October 1938 Waltrip could not meet his debts. In December Waltrip was demanding a higher salary, even with the shortfall in income. His Board of Directors quit and left him to deal with the finances. His solution was not to pay the mortgage or debts on the Chapel. Radio Chapel went into bankruptcy. Waltrip's last sermon was in May 1939. The Waltrips were on their own. Kathryn's happy vision of she and her husband flying back and forth between Denver and Mason City with a successful preaching careers was utterly demolished.
The next few years were very hard for the couple. They embarked on the road as traveling evangelists, primarily staying in the Midwest. They were not accepted in many places due to their marriage history. Initial advertisements listed Waltrip as the primary evangelist. Then occasionally Mrs. Waltrip was also mentioned. By the early 1940s Kathryn Kuhlman Waltrip was given equal billing. Finally by the mid-1940s Kathryn was using only Kathryn Kuhlman in meetings where she was the primary speaker. In 1944 Kuhlman went on an evangelistic tour on the east coast without Waltrip. It may have been a conscious decision to leave him, or she may also have taken the opportunity to reassess her life. It appears to have been more gradual as Waltrip wrote about them as a couple as late as 1946. Kuhlman never returned to Waltrip and they eventually divorced in 1947. She left her marriage behind and from then on acted as if it never existed in the first place.
In 1946 Kuhlman was asked to speak in Franklin, Pennsylvania. She was well received and decided to stay in the area. Kuhlman began preaching on radio broadcasts in Oil City, Pennsylvania. These became so popular they were picked up in Pittsburgh, and she was preaching throughout the area. She began to preach about the healing power of God. In 1947 a woman was healed of a tumor while listening to Kuhlman preach. Several Sundays later a man was also healed while she was teaching on the Holy Spirit. She was now convinced of God's healing work. One important thing to note is the context and timing of this breakout period in Kuhlman's life. 1947 was the beginning of the Healing Revival (sometimes referred to as the Latter Rain Revival) that would last for the next 10 years. What was happening in Kuhlman's meetings was breaking out across the United States. It was in this time frame that the Voice of Healing Ministry was established and men like William Branham, Oral Roberts, A.A. Allen and many others were propelled onto the public stage. Kuhlman was not associated with those groups, but stepped into the flow of what God's Spirit was doing across the nation and the world.
In 1948 Kuhlman held a series of meetings at Carnegie Hall in Pittsburgh. She eventually moved to Pittsburgh in 1950, and continued to hold meetings at Carnegie Hall until 1971. She was used by God to bring the charismatic message to many denominational churches, including the Catholic Church. (She received a lot of criticism over this and was accused of being a closet Catholic.) These were her best known years. Her style was flamboyant. She would hold her famous miracle services and the auditorium was filled to capacity every time. She was on radio and television shows. She was ordained in 1968 by the Evangelical Church Alliance. Hundreds of people were healed in her meetings, and even while listening to her on the radio or television. People she prayed for would often be hit with the power of God and be "slain in the Spirit." Kuhlman never claimed that she was the healer. She always pointed people to Jesus as their healer.
Kuhlman had been diagnosed with a heart problem in 1955. She kept a very busy schedule and overworked herself, especially in the 1970's. She traveled back and forth from Pittsburgh to Los Angeles frequently, as well as taking trips around the world. Her heart was enlarged and Kuhlman died on February 20, 1976, in Tulsa, following open-heart surgery. Videos of some of her services are still available and continue to be popular today.
Kathryn Johanna Kuhlman was born on May 9, 1907, in Concordia, Missouri. Her parents were German and she was one of four children. Her mother was a harsh disciplinarian, who showed little love or affection. On the other hand, she had an extremely close and loving relationship with her father. She would describe, as a small child how, her father would come home from work and she would hang on his leg and cling to him. She often said that her relationship with God the Father was extremely real because of her relationship with her own father.
Kuhlman was converted, when she was 14, at an evangelistic meeting held in a small Methodist church. When she was 16 she graduated from high school, which only went to tenth grade in their town. He older sister Myrtle had married an itinerant evangelist, Everett B. Parrott. They spent their time traveling and asked that Kathryn could join them for the summer. Her parents agreed and she went to Oregon to help out. She worked with them, and often gave her testimony. When the summer was over she wanted to stay, and the couple agreed. She ended up working with them for five years.
The evangelistic team was made up of four people, Everette, Myrtle, Kathryn, and pianists named Helen Gulliford. In 1928 Everette missed a meeting in Boise, Idaho. Myrtle and Kathryn preached to cover for Everette. The pastor of the church encouraged Kathryn to step out on her own. Helen agreed to join her. Her first sermon was in a run-down pool hall in Boise, Idaho. The team covered Idaho, Utah, and Colorado for the following five years. In 1933 they moved into Pueblo, Colorado. They set up in an abandoned Montgomery Ward warehouse. They stayed there for six months.
Denver, being a much bigger city, was the next stop. They moved several times but ended up in a paper company's warehouse, which they named the Kuhlman Revival Tabernacle. Then in 1935 they moved once more to an abandoned truck garage they named the Denver Revival Tabernacle. Kathryn was seeing a lot of success in Denver. The church grew to about 2000 members. She began a radio show called "Smiling Through" and invited speakers from all over the country. One of them was Phil Kerr who taught on divine healing. In 1935 another invited evangelist was Burroughs Waltrip.
Waltrip was bad news for Kuhlman. He was a charismatic, handsome man several years older than she was. There was an immediate attraction, and one family claims to have seen the couple embracing in 1935, but he was married and had two children. Waltrip left Denver and went home to Austin, Texas, but the relationship simmered between Kuhlman and Waltrip. In 1937 he was invited back to Denver to take the pulpit for two months. Shortly after he divorced his wife and abandoned his two sons. He then spread the story that his wife had left him. He moved to Mason City, Iowa, where he told everyone he was single, and started a new ministry. Waltrip raised pledges of $70,000 to build a ministry building called Radio Chapel. It was state of the art with a disappearing pulpit and an art deco style. He appeared to be a successful and dynamic preacher.
There was an ongoing relationship between Kuhlman and Waltrip, and they married in September 1938. Kuhlman was naive about the consequences of her choices and the marriage was a disaster. She announced to her church that she and Waltrip were married and they would go between Denver and Mason City preaching at their two churches. Most of the people in her congregation left due to her relationship with Waltrip. She gave up her church in Denver, lost some of her closest associates, and moved to Mason City. Waltrip's success turned out to be a pipe dream as well. The Radio Chapel was completed in June of 1938. By October 1938 Waltrip could not meet his debts. In December Waltrip was demanding a higher salary, even with the shortfall in income. His Board of Directors quit and left him to deal with the finances. His solution was not to pay the mortgage or debts on the Chapel. Radio Chapel went into bankruptcy. Waltrip's last sermon was in May 1939. The Waltrips were on their own. Kathryn's happy vision of she and her husband flying back and forth between Denver and Mason City with a successful preaching careers was utterly demolished.
The next few years were very hard for the couple. They embarked on the road as traveling evangelists, primarily staying in the Midwest. They were not accepted in many places due to their marriage history. Initial advertisements listed Waltrip as the primary evangelist. Then occasionally Mrs. Waltrip was also mentioned. By the early 1940s Kathryn Kuhlman Waltrip was given equal billing. Finally by the mid-1940s Kathryn was using only Kathryn Kuhlman in meetings where she was the primary speaker. In 1944 Kuhlman went on an evangelistic tour on the east coast without Waltrip. It may have been a conscious decision to leave him, or she may also have taken the opportunity to reassess her life. It appears to have been more gradual as Waltrip wrote about them as a couple as late as 1946. Kuhlman never returned to Waltrip and they eventually divorced in 1947. She left her marriage behind and from then on acted as if it never existed in the first place.
In 1946 Kuhlman was asked to speak in Franklin, Pennsylvania. She was well received and decided to stay in the area. Kuhlman began preaching on radio broadcasts in Oil City, Pennsylvania. These became so popular they were picked up in Pittsburgh, and she was preaching throughout the area. She began to preach about the healing power of God. In 1947 a woman was healed of a tumor while listening to Kuhlman preach. Several Sundays later a man was also healed while she was teaching on the Holy Spirit. She was now convinced of God's healing work. One important thing to note is the context and timing of this breakout period in Kuhlman's life. 1947 was the beginning of the Healing Revival (sometimes referred to as the Latter Rain Revival) that would last for the next 10 years. What was happening in Kuhlman's meetings was breaking out across the United States. It was in this time frame that the Voice of Healing Ministry was established and men like William Branham, Oral Roberts, A.A. Allen and many others were propelled onto the public stage. Kuhlman was not associated with those groups, but stepped into the flow of what God's Spirit was doing across the nation and the world.
In 1948 Kuhlman held a series of meetings at Carnegie Hall in Pittsburgh. She eventually moved to Pittsburgh in 1950, and continued to hold meetings at Carnegie Hall until 1971. She was used by God to bring the charismatic message to many denominational churches, including the Catholic Church. (She received a lot of criticism over this and was accused of being a closet Catholic.) These were her best known years. Her style was flamboyant. She would hold her famous miracle services and the auditorium was filled to capacity every time. She was on radio and television shows. She was ordained in 1968 by the Evangelical Church Alliance. Hundreds of people were healed in her meetings, and even while listening to her on the radio or television. People she prayed for would often be hit with the power of God and be "slain in the Spirit." Kuhlman never claimed that she was the healer. She always pointed people to Jesus as their healer.
Kuhlman had been diagnosed with a heart problem in 1955. She kept a very busy schedule and overworked herself, especially in the 1970's. She traveled back and forth from Pittsburgh to Los Angeles frequently, as well as taking trips around the world. Her heart was enlarged and Kuhlman died on February 20, 1976, in Tulsa, following open-heart surgery. Videos of some of her services are still available and continue to be popular today.
if you could see the end - the story god writes in suffering
A strange grief crept upon me as the final Lord of the Rings movie came to an end. An unliterary man at the time, I watched the doors to Middle Earth close. The story would not continue. A sense of silliness accompanied the sadness. Why should a boy, let alone a young man, lament saying goodbye to an imaginary friend whom he knew all along to be imaginary? This is exactly what great stories do to us. Whether captured on screen or between covers of a book, to finally arrive at the end can seem as though palace doors were closing to us. The adventure concludes — with all its dangers, losses, courage, companionship, thrill, and great loves worth living and dying for. They leave us again, to our world. As credits roll, we are made to feel like we are leaving the momentous, the beautiful, the good, and returning to, well, the ordinary. But what if the ache one feels at the conclusion of these tales, the bitter loss in the happily ever after, is not unreality mocking, but Reality inviting? Keep Your Hobbitry What if epic stories cast a spell, not because they are fictional, but because they stir suppressed longings that we just might, in fact, live in such a Story? Perhaps we all hunger to be characters in a grand Story, a heroic tale, a high Romance, a story without end. “He has,” after all, “put eternity into man’s heart” (Ecclesiastes 3:11). The lines between our favorite stories and our own story in this life may be thinner than we have yet dreamed. J.R.R. Tolkien himself captures this in a letter to his son, Christopher, who was serving in the Air Force during World War II: Well, there you are: a hobbit amongst the Urukhai [a deadly enemy]. Keep your hobbitry in heart, and think that all stories feel like that when you are in them. You are inside a very great story! (183) Do you know yourself to be in a very great story? Do the elves and kings, the lovers and heroes, the characters of your favorite tales have a right to envy you? Until we smile at and embrace the story we find ourselves in, we will not have the hope, the joy, the strength to live to the fullest in this life — and then everlastingly in the next. Designed for Story We are a people of story — delighted by them, taught by them, shaped by them. We starve for meaning. We long for dots to connect. For a golden Thread to run through. Otherwise, we are left in bitter realms of nothingness. “We are a people of story — delighted by them, taught by them, shaped by them.” To reckon with life among us, we search for the Story beyond us. From the beginning, many claimed to do just that. Different prophets from different peoples brought down different explanations from tall mountains to interpret the joys and horrors, hills and valleys, sunrays and shadows of this life. Ancient myths rode to meet ancient desires not so easily filled in hearts hungering for forever. Shared stories made up culture. Shared stories made up religion. Men lived from story and died for story — stories designed to provide answers to life’s biggest questions. And hope needs answers that Story provides. The marketplace is full of stories, of worldviews trying to answer those great questions for us. Andrew Delbanco, in his meditation on hope, identifies that the general narrative that united Americans has shifted from a story about God, to that of nation, to that of self. We have moved from the cross, to the flag, and now landed on the narrow and perilous path of me . Of all people at all times, none has been more driven by story than followers of Christ. Even if an angel came down from heaven with a new story, we would refuse it with disdain (Galatians 1:8). And yet, while we often remain orthodox, despair still emerges when we focus solely on the real sadness in our single sentence called life, and our hearts forget the tale beyond. Hope, however, considers that sentence in the whole Story, a Story written by one who did not spare his own Son. Hope reaches past the groans, for that part of the Story with no more sin, no more suffering, no more separation. Joseph: A Case Study Hope stays attuned to God’s Story, because it withers with forgetting. Take as a test case of someone who didn’t sink in the swamp of self, an Old Testament man of God, Joseph. His life is full of many valleys. Betrayed, assaulted, and sold into slavery, Joseph found himself in Potiphar’s house. After being exalted to Potiphar’s right hand, Joseph is sexually harassed, falsely accused, and sent to prison. After correctly interpreting one of Pharaoh’s servant’s dreams, he is betrayed and forgotten. And then after two more long years in prison, he is exalted to become “a father to Pharaoh” (Genesis 45:8). His human story — full of abuse, betrayal, accusation, and lies — fell purposefully within God’s bigger story, and he knew it . When he reveals his identity to his brothers who sold him, he says to his brothers, “Come near to me, please.” And they came near. And he said, “I am your brother, Joseph, whom you sold into Egypt. And now do not be distressed or angry with yourselves because you sold me here, for God sent me before you to preserve life. For the famine has been in the land these two years, and there are yet five years in which there will be neither plowing nor harvest. And God sent me before you to preserve for you a remnant on earth, and to keep alive for you many survivors. So it was not you who sent me here, but God . He has made me a father to Pharaoh, and lord of all his house and ruler over all the land of Egypt.” (Genesis 45:4–8) He and his brothers knew his story. Twice he acknowledges what was obvious to them all: “ You sold me here.” Joseph had not forgotten the nights — the years — in prison away from friends and family, the horror of their closing ears to his pleading as they cast him in the pit, their cruelty to sell him to those who would mistreat and perhaps murder him. The darkness, though past, was still dark. Memories remained. But when he calls them near, he remembers more than just his story as seen from ground level — and this gives power to forgive and love his guilty brothers. He tells them not to be distressed or angry with themselves. Why? “ For God sent me before you to preserve life.” In their selling, God was sending. In their evil, God intended good. In the darkest scene of the play, God was still writing. That Story smothered bitterness and revenge. That Story and its Author allowed him to forgive, bless, and love where a different story would have had him calculate the wrongs, grip firmly the treachery, and use his power to exact revenge. And the Story gave him hope for the future promises of his God, recorded as the radiant triumph of his life in Hebrews 11: “By faith Joseph, at the end of his life, made mention of the exodus of the Israelites and gave directions concerning his bones” (Hebrews 11:22). He knew, as those of us who fall asleep in the Lord do as well, that we shall wake in the Promised Land. When Elves Envy Men Although it may not feel like it, we live in a very great story. Have we forgotten? “We, in America, have moved from the cross, to the flag, and now landed on the narrow and perilous path of me.” Our hearts grow accustomed to the extraordinary as it becomes familiar. We lose a sense of where we live when we can drive home without a map. Life no longer invigorates. God’s epic plays out all around us, and he draws us in to play our part, and yet we halfheartedly read our lines or escape into other people’s lives. We are bored. But awake, we live in a great Story. Wild and throbbing with adventure, trying and terrible at parts. Eternity hanging in the balance. A fierce Dragon threatens. Demons surround. Hell gapes. The Light still shines in the darkness. Angels assemble. The Spirit animates. Christians stand clad in armor. The church marches on hades. Judgment hastens. Salvation is ready to be revealed. The True King — whose sandals no other character is worthy to unlatch — has died for sinners and lives forevermore. He is coming. This tale plays out on earth in what we blaspheme and call “ordinary.” With all its details and drudgery, its paying bills and crying babies, its baseball games and rush-hour traffic, an eternal drama plays. One that draws heaven’s attention. Angels ache to leave the theater. You are on the inside of a very great Story — a story to be remembered, cherished, and clung to during the most difficult scenes. Is there any other tale you would rather find was true?