Others like seed of wisdom Features >>
.mobi-160.webp)
The 3 Most Important Things In Your Life
-160.webp)
Finding Your Purpose In Life (Why Am I Here)

The Assignment Vol 3: The Trials And The Triumphs

The Assignment Vol I: The Dream And The Destimy

The Assignment Vol 2: The Anointing And The Adversity

The Assignment Vol 4: The Pain And The Passion

Wisdom From Myles Munroe

The Wisdom Of Making Right Choices

The End Of Me

Awakening Mystical Consciousness
About the Book
"Seed Of Wisdom" by Mike Murdock is a book that explores the concept of sowing seeds of kindness, generosity, and love in order to reap the rewards of a fulfilled and abundant life. The author emphasizes the importance of cultivating positive traits and behaviors in order to achieve success and happiness in all areas of life. Through personal anecdotes and biblical teachings, Murdock encourages readers to invest in their personal growth and relationships through the planting of "seeds" of wisdom.
John Alexander Dowie
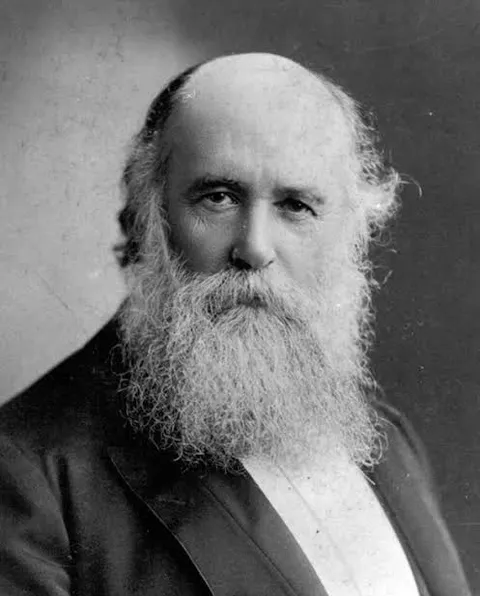 By John Alexander Dowie (1847 – 1907)
I sat in my study in the parsonage of the Congregational Church at Newtown, a suburb of the beautiful city of Sydney, Australia. My heart was very heavy, for I had visited the sick and dying beds of more than thirty of my flock, and I had cast the dust to its kindred dust into more than forty graves within a few weeks. Where, oh where, was He Who used to heal His suffering children? No prayer for healing seemed to reach His ear, and yet I knew His hand had not been shortened. Still it did not save from death even those for whom there was so much in life to live for God and others. Strong men, fathers, good citizens, and more than all, true Christians sickened with a putrid fever, suffered nameless agonies, passed into delirium, sometimes with convulsions, and then died.
Oh, what aching voids were left in many a widowed or orphaned heart. There were many homes where, one by one, the little children, the youths and the maidens lay stricken, and after a hard struggle with the foul disease, they too, lay cold and dead. It seemed sometimes as if I could almost hear the triumphant mockery of evil ringing in my ear whilst I spoke to the bereaved ones the words of Christian hope and consolation. Disease, the foul offspring of its father, Satan, and its mother Sin, was defiling and destroying the earthly temples of God’s children and there was no deliverance.
There I sat with sorrow-bowed head for my afflicted people, until the bitter tears came to relieve my burning heart. Then I prayed for some message, and oh, how I longed to hear some words from Him Who wept and sorrowed for the suffering long ago, a Man of Sorrows and Sympathies. The words of the Holy Ghost inspired In Acts 10:38, stood before me all radiant with light, revealing Satan as the Defiler, and Christ as the Healer. My tears were wiped away, my heart strong, I saw the way of healing, and the door thereto was opened wide, so I said, “God help me now to preach the Word to all the dying around, and tell them how Satan still defiles, and Jesus still delivers, for He is just the same today.”
A loud ring and several raps at the outer door, a rush of feet, and there at my door stood two panting messengers who said, “Oh, come at once, Mary is dying; come and pray. “With just a feeling as a shepherd has who hears that his sheep are being torn from the fold by a cruel wolf, I rushed from my house, ran without my hat down the street, and entered the room of the dying maiden. There she lay groaning and grinding her clenched teeth in the agony of the conflict with the destroyer. The white froth, mingled with her blood, oozing from her pale and distorted mouth. I looked at her and then my anger burned. “Oh,” I thought, “for some sharp sword of heavenly temper keen to slay this cruel foe who is strangling that lovely maiden like an invisible serpent, tightening his deadly coils for a final victory.”
In a strange way, It came to pass; I found the sword I needed was in my hands, and in my hand I hold it still and never will I lay It down. The doctor, a good Christian man, was quietly walking up and down the room, sharing the mother’s pain and grief. Presently he stood at my side and said, “Sir, are not God’s ways mysterious?” Instantly the sword was flashed in my hand, the Spirit’s sword, the Word of God. “God’s way?!” I said, pointing to the scene of conflict, “How dare you call that God’s way of bringing His children home from earth to Heaven? No sir, that is the devil’s work and it is time we called on Him Who came to destroy the work of the devil, to slay that deadly foul destroyer, and to save this child. Can you pray, Doctor, can you pray the prayer of faith that saves the sick?” At once, offended at my words, my friend was changed, and saying,” You are too much excited, sir, it is best to say ‘God’s will be done,’” and he left the room.
Excited?! The word was quite inadequate for I was almost frenzied with divinely imparted anger and hatred of that foul destroyer, disease, which was doing Satan’s will. “It is not so,” I exclaimed, “no will of God sends such cruelty, and I shall never say ‘God’s will be done’ to Satan’s works, which God’s own Son came to destroy, and this is one of them.” Oh, how the Word of God was burning in my heart: “Jesus of Nazareth went about doing good, and healing all that were oppressed of the devil; for God was with Him.” And was not God with me? And was not Jesus there and all His promises true? I felt that it was even so, and turning to the mother I inquired,” Why did you send for me?” To which she answered, “Do pray, oh pray for her that God may raise her up.” So we prayed.
What did I say? It may be that I cannot recall the words without mistake, but words are in themselves of small importance. The prayer of faith may be a voiceless prayer, a simple heartfelt look of confidence into the face of Christ. At such moment, words are few, but they mean much, for God is looking at the heart. Still, I can remember much of that prayer unto this day, and asking God to aid, I will attempt to recall it. I cried, “Our Father, help! and Holy Spirit, teach me how to pray. Plead Thou for us, oh, Jesus, Savior, Healer, Friend, our Advocate with God the Father. Hear and heal, Eternal One! From all disease and death, deliver this sweet child of yours. I rest upon the Word. We claim the promise now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord that heals thee.’ Then heal her now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord, I change not.’ Unchanging God, then prove Yourself the healer now. The Word is true. ‘These signs shall follow them that believe in My Name, they shall lay hands on the sick, and they shall recover.’ And I believe and I lay hands in Jesus’ Name on her and claim this promise now. Your Word is true. ‘The prayer of faith shall save the sick. Trusting in You alone. I cry. Oh, save her now, for Jesus’ sake. Amen!”
Then, the maid lay in sleep so deep and sweet that the mother asked in a low whisper, “Is she dead?” “No,” I answered, in a whisper lower still. “Mary will live; the fever is gone. She is perfectly well and sleeping as an infant sleeps.” I was smoothing the long dark hair from her now peaceful brow, and feeling the steady pulsation of her heart and cool moist hands. I saw that Christ had heard, and that once more, as long ago in Peter’s house, “He touched her and the fever left her.” Turning to the nurse, I said, “Get me at once, please, a cup of cocoa and several slices of bread and butter.” Beside the sleeping maid we sat quietly and almost silently until the nurse returned, and then I bent over her and snapping my fingers called, “Mary!”
Instantly she woke, smiled and said, “Oh, sir, when did you come? I have slept so long;” then stretching her arms out to meet her mother’s embrace, she said, “Mother, I feel so well.” “And hungry, too?” I asked, pouring some of the cocoa in a saucer and offering it to her when cooled by my breath. “Yes, hungry too,” she answered with a little laugh, and drank and ate again, and yet again until all was gone. In a few minutes, she fell asleep, breathing easily and softly. Quietly thanking God. We left her bed and went to the next room where her brother and sister also lay sick of the same fever. With these two, we prayed and they were healed too. The following day all three were well and in a week or so they brought me a little letter and a gift of gold, two sleeve links with my monogram, which I wore for many years. As I went away from the home where Christ as the Healer had been victorious, I could not but have somewhat in my heart of the triumphant song that rang through Heaven, and yet I was not a little amazed at my own strange doings, and still more at my discovery that He is just the same today.
Excerpt from the Sermons of John Alexander Dowie Champions of Faith by Gordon Lindsay
By John Alexander Dowie (1847 – 1907)
I sat in my study in the parsonage of the Congregational Church at Newtown, a suburb of the beautiful city of Sydney, Australia. My heart was very heavy, for I had visited the sick and dying beds of more than thirty of my flock, and I had cast the dust to its kindred dust into more than forty graves within a few weeks. Where, oh where, was He Who used to heal His suffering children? No prayer for healing seemed to reach His ear, and yet I knew His hand had not been shortened. Still it did not save from death even those for whom there was so much in life to live for God and others. Strong men, fathers, good citizens, and more than all, true Christians sickened with a putrid fever, suffered nameless agonies, passed into delirium, sometimes with convulsions, and then died.
Oh, what aching voids were left in many a widowed or orphaned heart. There were many homes where, one by one, the little children, the youths and the maidens lay stricken, and after a hard struggle with the foul disease, they too, lay cold and dead. It seemed sometimes as if I could almost hear the triumphant mockery of evil ringing in my ear whilst I spoke to the bereaved ones the words of Christian hope and consolation. Disease, the foul offspring of its father, Satan, and its mother Sin, was defiling and destroying the earthly temples of God’s children and there was no deliverance.
There I sat with sorrow-bowed head for my afflicted people, until the bitter tears came to relieve my burning heart. Then I prayed for some message, and oh, how I longed to hear some words from Him Who wept and sorrowed for the suffering long ago, a Man of Sorrows and Sympathies. The words of the Holy Ghost inspired In Acts 10:38, stood before me all radiant with light, revealing Satan as the Defiler, and Christ as the Healer. My tears were wiped away, my heart strong, I saw the way of healing, and the door thereto was opened wide, so I said, “God help me now to preach the Word to all the dying around, and tell them how Satan still defiles, and Jesus still delivers, for He is just the same today.”
A loud ring and several raps at the outer door, a rush of feet, and there at my door stood two panting messengers who said, “Oh, come at once, Mary is dying; come and pray. “With just a feeling as a shepherd has who hears that his sheep are being torn from the fold by a cruel wolf, I rushed from my house, ran without my hat down the street, and entered the room of the dying maiden. There she lay groaning and grinding her clenched teeth in the agony of the conflict with the destroyer. The white froth, mingled with her blood, oozing from her pale and distorted mouth. I looked at her and then my anger burned. “Oh,” I thought, “for some sharp sword of heavenly temper keen to slay this cruel foe who is strangling that lovely maiden like an invisible serpent, tightening his deadly coils for a final victory.”
In a strange way, It came to pass; I found the sword I needed was in my hands, and in my hand I hold it still and never will I lay It down. The doctor, a good Christian man, was quietly walking up and down the room, sharing the mother’s pain and grief. Presently he stood at my side and said, “Sir, are not God’s ways mysterious?” Instantly the sword was flashed in my hand, the Spirit’s sword, the Word of God. “God’s way?!” I said, pointing to the scene of conflict, “How dare you call that God’s way of bringing His children home from earth to Heaven? No sir, that is the devil’s work and it is time we called on Him Who came to destroy the work of the devil, to slay that deadly foul destroyer, and to save this child. Can you pray, Doctor, can you pray the prayer of faith that saves the sick?” At once, offended at my words, my friend was changed, and saying,” You are too much excited, sir, it is best to say ‘God’s will be done,’” and he left the room.
Excited?! The word was quite inadequate for I was almost frenzied with divinely imparted anger and hatred of that foul destroyer, disease, which was doing Satan’s will. “It is not so,” I exclaimed, “no will of God sends such cruelty, and I shall never say ‘God’s will be done’ to Satan’s works, which God’s own Son came to destroy, and this is one of them.” Oh, how the Word of God was burning in my heart: “Jesus of Nazareth went about doing good, and healing all that were oppressed of the devil; for God was with Him.” And was not God with me? And was not Jesus there and all His promises true? I felt that it was even so, and turning to the mother I inquired,” Why did you send for me?” To which she answered, “Do pray, oh pray for her that God may raise her up.” So we prayed.
What did I say? It may be that I cannot recall the words without mistake, but words are in themselves of small importance. The prayer of faith may be a voiceless prayer, a simple heartfelt look of confidence into the face of Christ. At such moment, words are few, but they mean much, for God is looking at the heart. Still, I can remember much of that prayer unto this day, and asking God to aid, I will attempt to recall it. I cried, “Our Father, help! and Holy Spirit, teach me how to pray. Plead Thou for us, oh, Jesus, Savior, Healer, Friend, our Advocate with God the Father. Hear and heal, Eternal One! From all disease and death, deliver this sweet child of yours. I rest upon the Word. We claim the promise now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord that heals thee.’ Then heal her now. The Word is true, ‘I am the Lord, I change not.’ Unchanging God, then prove Yourself the healer now. The Word is true. ‘These signs shall follow them that believe in My Name, they shall lay hands on the sick, and they shall recover.’ And I believe and I lay hands in Jesus’ Name on her and claim this promise now. Your Word is true. ‘The prayer of faith shall save the sick. Trusting in You alone. I cry. Oh, save her now, for Jesus’ sake. Amen!”
Then, the maid lay in sleep so deep and sweet that the mother asked in a low whisper, “Is she dead?” “No,” I answered, in a whisper lower still. “Mary will live; the fever is gone. She is perfectly well and sleeping as an infant sleeps.” I was smoothing the long dark hair from her now peaceful brow, and feeling the steady pulsation of her heart and cool moist hands. I saw that Christ had heard, and that once more, as long ago in Peter’s house, “He touched her and the fever left her.” Turning to the nurse, I said, “Get me at once, please, a cup of cocoa and several slices of bread and butter.” Beside the sleeping maid we sat quietly and almost silently until the nurse returned, and then I bent over her and snapping my fingers called, “Mary!”
Instantly she woke, smiled and said, “Oh, sir, when did you come? I have slept so long;” then stretching her arms out to meet her mother’s embrace, she said, “Mother, I feel so well.” “And hungry, too?” I asked, pouring some of the cocoa in a saucer and offering it to her when cooled by my breath. “Yes, hungry too,” she answered with a little laugh, and drank and ate again, and yet again until all was gone. In a few minutes, she fell asleep, breathing easily and softly. Quietly thanking God. We left her bed and went to the next room where her brother and sister also lay sick of the same fever. With these two, we prayed and they were healed too. The following day all three were well and in a week or so they brought me a little letter and a gift of gold, two sleeve links with my monogram, which I wore for many years. As I went away from the home where Christ as the Healer had been victorious, I could not but have somewhat in my heart of the triumphant song that rang through Heaven, and yet I was not a little amazed at my own strange doings, and still more at my discovery that He is just the same today.
Excerpt from the Sermons of John Alexander Dowie Champions of Faith by Gordon Lindsay
the only certain hope on earth
“It is the hope that kills you,” as many English football (soccer) fans say. Is it not better to have low expectations instead of hoping your team will do well, only to see those hopes dashed in sometimes cruel ways? The world has an idea of hope that sees it as an optimistic expectation that something good may happen in this life or, for the religious, the life to come. People cannot help but hope; it is part of our DNA as humans. We hope for good health, a good marriage, good weather, or an enjoyable holiday. Many even hope for a better life after the life they have lived on earth, which explains why so many claim that loved ones (including animals) are “smiling down” upon them after their death. Much of the hope that is found in the world lacks promise and certainty, which is like building a house on sand. Christian hope is very different from worldly hope. Christian hope is a Spirit-given virtue enabling us to joyfully expect what God has promised through Jesus Christ. It is, therefore, thoroughly Trinitarian. Height of Our Hope Christian hope looks to God because he is “the God of hope” (Romans 15:13). Because of the resurrection of Christ, Peter says that our “faith and hope are in God” (1 Peter 1:21). The degree to which we find God desirable and excellent will be the same to which hope plays a role in our lives. Our view of God will affect the hope we possess. A small god begets a small hope; but knowing God and Christ (John 17:3), which is eternal life, is ground for possessing a hope that bursts forth in our souls on a daily basis. The psalmist describes the blessed person as the one “whose help is the God of Jacob, whose hope is in the Lord his God” (Psalm 146:5). Consider the words of Thomas Aquinas on this: Wherefore the good which we ought to hope for from God properly and chiefly is the infinite good, which is proportionate to the power of our divine helper, since it belongs to an infinite power to lead anyone to an infinite good. Such a good is eternal life, which consists in the enjoyment of God Himself. For we should hope from Him for nothing less than Himself, since His goodness, whereby He imparts good things to His creature, is no less than His essence . Therefore the proper and principal object of hope is eternal happiness. ( Summa Theologica , II-II.17.2) In short, Aquinas is saying that our joy is connected to our hope, which is connected to our Savior, which is connected to our God. Christian hope exists only when we hope in the God and Father of our Lord Jesus Christ (1 Peter 1:13). The height of our hope is God himself. Certain as God’s Promises Certain conditions characterize biblical hope: it must be good, it must be in the future, it involves some degree of difficulty (for example, patient suffering), and it must be founded on God’s promises. Those who persevere, by faith, shall attain what we hope for: the sight of our Savior (Titus 2:13). “Christian hope is a Spirit-given virtue enabling us to joyfully expect what God has promised through Jesus Christ.” This hope of the blessed vision of Christ is based not only upon the fact that we know he will return, but also on the knowledge that God dwells in us. This explains Paul’s language in Romans 15:13, “May the God of hope fill you with all joy and peace in believing, so that by the power of the Holy Spirit you may abound in hope.” Hope arises from not only objective promises, but also an internal “pull” toward God and Christ by his Spirit. Thus, Christian hope is not about probable hope or about mere conjecture concerning things future, but about great certainty. Faith, Hope, and Love Faith in God through Christ by the Spirit gives rise to Christian hope. Faith and hope bear an intimate relation to one another (Romans 4:18–21; 5:2; 15:13; Galatians 5:5; Ephesians 1:18–19; Colossians 1:23; 1 Timothy 4:10; Hebrews 11:1; 1 Peter 1:21). Faith is the foundation of hope, so that hope without faith is no hope at all. We believe God in order to hope in what we believe. But faith also returns to hope to give it courage to persevere. If faith apprehends God’s promises, hope expects what he promises. In times of trouble, despair, and suffering, faith and hope feed on God and his promises. The difference between faith and hope is not easy to discern. Simply put, faith believes, but hope waits patiently. (Yet there is an aspect whereby faith also requires patience.) God is the object of hope, as it specifically focuses on his goodness to us in Christ. Faith not only looks to God but also trembles at his threatenings (when appropriate). Hope remains free of such fear. Faith and love can relate to a present or future object, but hope looks to the future alone. And of course, faith and hope also bear an intimate relation to love. If hope relates to faith in terms of our expectations, hope relates to love in terms of our desire. Love requires desire, so the more we desire the good, the more we will love it. Equally, hope requires desire. The more we desire what is promised, the more we hope for it. Since faith focuses on Christ, hope will always be present where there is true faith. And since faith focuses on Christ, love will always accompany faith and hope because God and Christ are the object of faith and hope — how can we not love the one we believe has saved us and promised so much for the future? Thus, faith, hope, and love give expression to our Christian life (1 Corinthians 13:13; Colossians 1:4). Hope That Purifies The life of hope yields many benefits to the Christian, such as the expectation of eternal life (Titus 1:2; 3:7), salvation (1 Thessalonians 5:8), heaven (Colossians 1:5), the resurrection (Acts 23:6), the gospel (Colossians 1:23), God’s calling (Ephesians 1:18; 4:4), and our inheritance (Ephesians 1:18). But there is also a “duty” bound up with hope, namely, purification of our souls: “Everyone who thus hopes in him purifies himself as he is pure” (1 John 3:3). This command follows one of the greatest promises of Christian hope: “Beloved, we are God’s children now, and what we will be has not yet appeared; but we know that when he appears we shall be like him, because we shall see him as he is” (1 John 3:2). Those who have the hope of being made like Christ in body and soul must also have the present desire to be pure . While in sanctification the accent is often on what God does, here in 1 John 3:3 the accent is on what we do. Christians, if they embrace a hope of seeing Christ face to face, are to purify themselves. In other words, hope has a moral effect. The pursuit of purity arises out of our possession of hope. Hope gives birth to sanctification; and as we are sanctified, we hope even more because we get closer to God. Besides John, Peter also makes this point. He speaks of the future promise of the new heavens and new earth to his readers (2 Peter 3:13), and then reasons, “Therefore, beloved, since you are waiting for these, be diligent to be found by [God] without spot or blemish, and at peace” (2 Peter 3:14). “Our joy is connected to our hope, which is connected to our Savior, which is connected to our God.” Likewise, Paul writes, “Since we have these promises, beloved, let us cleanse ourselves from every defilement of body and spirit, bringing holiness to completion in the fear of God” (2 Corinthians 7:1). The promises Paul speaks of include our adoption as sons and daughters, wherein God makes his dwelling and walks among us (2 Corinthians 6:16, 18). These promises are, of course, realized in this life, but they also await a type of consummation that we can all look forward to (see Romans 8:23). Christian hope has present realities, one of which includes our sanctification. In this matter, our faith clings ever so tightly to our hope, as we seek to be holy as God is holy. Hope Unlike the World’s In the church today, we have underemphasized the future motivation (our Christian hope) for how to live the sanctified life. As with the Lord’s Supper, we do not only look back to Christ’s death but also look now to the risen Christ and forward to the future blessings that await us. This is the purification of the truly hopeful. Our hope is unlike the world’s. The world’s hope is often vague, uncertain, a wish thrust up at the stars. But Christian hope is solid, certain, future, and cleansing. It lasts as long as the eternal God lives, and stands as tall as he stands. He is our hope, for apart from him, no such thing exists (Ephesians 2:13).



